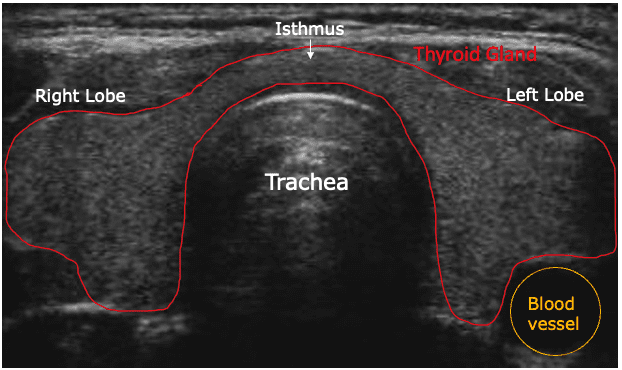
Thyroid ultrasound
It is the non-invasive medical imaging test which makes use of high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the thyroid gland or its surrounding tissues. It diagnoses and monitors numerous conditions, including:
- Nodules or cysts
- Enlargement of the thyroid (goiter)
- Inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis)
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Cancer of the thyroid
- Parathyroid disorders.
Information gathered from thyroid ultrasound includes:
1. Size and shape of the thyroid gland
2. Presence, size, number, and location of nodule or cyst
3. Texture and echogenicity of thyroid tissue
4. Blood flow and vascularization
5. Location and presence of parathyroid glands
6. Thyroid lesions or tumors
7. Thyroiditis or inflammation
8. Characterization of thyroid nodules or masses as benign or malignant
9. Vascularity and blood flow in the thyroid gland
10. Stiffness of the thyroid gland, elastography
The use of ultrasound of the thyroid is for diagnosing and monitoring a wide array of disorders of the thyroid, including:
1. Thyroid nodules or cysts
2. Cancer of the thyroid
3. Thyroiditis, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease
4. Hyperthyroidism
5. Hypothyroidism
6. Goiter-an enlarged thyroid
7. Parathyroid disorders-hyperparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism
8. Thyroiditis-inflammation
9. Thyroid abscess
10. Thyroid lesions, benign as well as malignant.
The health care providers can find thyroid ultrasounds valuable for:
1. To evaluate thyroid nodules and masses
2. To guide fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB)
3. To monitor the change in the size or shape of the thyroid
4. For detecting thyroid inflammation as well as infection
5. Evaluation of parathyroid gland function
6. Follow-up of surgery on the thyroid or radiofrequency ablation
7. Long-term monitoring for thyroid cancer treatment response
What Is a Thyroid ultrasound ?
A thyroid ultrasound is a painless, non-invasive medical imaging test that produces detailed images of the thyroid gland and surrounding tissues using high-frequency sound waves. This is a diagnostic test, which helps diagnose and monitor different conditions within the thyroid gland.
A probe known as a transducer is placed on the neck during a thyroid ultrasound, and it sends sound waves that travel to the thyroid gland. The transducer captures the echoes and transmits them to the computer for the creation of images of the thyroid gland and its tissues.
Thyroid ultrasound is used for:
-A great way to assess thyroid nodules or masses
-Assist in guiding fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB)
-Monitoring a size or shape of the thyroid
-Detect thyroid inflammation or infection
It is helpful for the evaluation of the function of the parathyroid gland and guides thyroid surgery or radiofrequency ablation and monitoring in response to the treatment of thyroid cancer.
Thyroid ultrasound is one of the most widely used instruments by healthcare providers as an aid in assessment and management of the health of the thyroid. It is particularly useful to assess nodularity in the thyroid, monitor the response of thyroid cancer, and guide biopsy or surgery.
There are several types of thyroid ultrasound:
– Real-time ultrasound
– Doppler ultrasound
– Color Doppler ultrasound
– Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
– Elastography (assesses tissue stiffness)
Reasons for a Thyroid Ultrasound:
- Detecting nodules or lumps: To evaluate any abnormalities, such as nodules, cysts, or lumps that may be found during a physical examination.
- Monitoring thyroid conditions: It can help in tracking changes in size or appearance of thyroid nodules over time.
- Diagnosing goiter: It helps in identifying enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Guiding fine needle aspiration: If a nodule is suspicious, an ultrasound may guide a needle biopsy to the collect tissue samples.
Procedure:
- The patient lies on their back with the neck extended.
- A gel is applied to the neck, or the handheld transducer is moved over the thyroid area.
- The transducer sends sound waves into the body, or the echoes are converted into images.
- The procedure typically takes 20-30 minutes and is painless.
What is procedures of Thyroid ultrasound ?
The steps followed to do thyroid ultrasound include:
1. Preparation
– No preparation is required for the test
– Remove any jewelry, as well as clothing that may interfere with the test
2. Positioning
– Lie on your back, rest your neck on extension
– A pillow or pad may be placed under your neck to support it
3. Transducer placement
– A small probe is placed over a thyroid gland on your neck
– Application of skin gel or oil to improve quality image
4. Scanning
– The transducer is transmitting or a receiving the reflected sound waves, which are then reconstructed as images on a monitor. The sonographer can maneuver the transducer to get images from all angles.
5. Doppler scan
– It studies blood circulation in the gland and also other soft tissue structures within the neck.
6. Elastography if required
– It studies tissue stiffness that may be helpful in differentiation between benign and malignant lesions.
7. Image interpretation
– Sonographer or radiologist reads images and measurements
8. Reporting:
– A report is prepared with the outcome or a recommended follow-up
9. Biopsy or further testing if appropriate:
– FNAB or other diagnostic tests would be ordered as appropriate based upon what is discovered by the ultrasound
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
