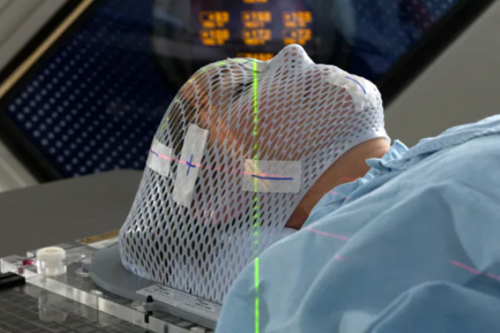
Stereotactic Surgery
Stereotactic Surgery In Nagpur (SRS) is a non-invasive medical treatment that uses several focus beams of radiation in order to treat the conditions of brain, neck, lungs, liver, vertebrae, and other body parts. As no incision or surgical approach is involved, it’s not surgical in nature. It actually uses 3D imaging for the correct targeting of high doses of radiation at the site of treatment to ensure minimal damage to the tissues surrounding it.
This technique functions through targeting the DNA in the targeted cells. Because, it destroys their replication capacity and leads to the diminution of tumor mass.
Types of Stereotactic Surgery In Nagpur
There are several types of stereotactic radiosurgery. The following lists a few of them: Gamma Knife Stereotactic radiosurgery is mainly for intracranial tumors and intracranial conditions.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) Stereotactic body radiation is utilized in the treatment of small tumorous lesions located in the lungs, liver, prostate, pancreas, and other sites.
Proton therapy (also known as particle beam radiation therapy): This technique involves the delivery of concentrated beams of high-energy particles to the body. thus, often used for the treatment of central nervous system cancers and any kind of tumors in other body parts.
Linear accelerator (LINAC): This machine is providing image-guide radiation therapy (IGRT) and intensity-modulate radiation therapy (IMRT).they deliver accurate treatment for tumors and cancers.
Key Features of Stereotactic Surgery:
- High Precision: Stereotactic surgery uses imaging techniques like MRI, CT, or PET scans to create detailed, three-dimensional maps of the brain or other areas being treated.
- Minimally Invasive: It involves making very small incisions or even no incisions (in the case of radiosurgery), minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Image-Guided: Surgeons rely on real-time imaging to guide their instruments to the exact location of the target area, improving accuracy and outcomes.
Uses of Stereotactic Surgery:
- Brain Tumors
- Stereotactic surgery allows for the precise removal or biopsy of brain tumors, particularly those located deep within the brain or in areas that are difficult to access with traditional surgery.
- Techniques like stereotactic biopsy involve removing a small sample of the tumor for diagnosis without needing a large incision.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
- A non-invasive form of stereotactic surgery that uses focused radiation beams to destroy abnormal tissues, such as tumors or blood vessel malformations, without making any incisions.
- Examples of SRS technologies include:
- Gamma Knife: Used primarily for brain tumors and functional disorders.
- CyberKnife: Can be used for both brain and body tumors, delivering high-dose radiation with precision.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
- A surgical treatment for movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
- In DBS, stereotactic techniques are used to place electrodes in specific brain areas. These electrodes deliver electrical impulses to regulate abnormal activity and improve motor symptoms.
- Epilepsy Surgery
- Stereotactic surgery is used to locate and remove or destroy areas of the brain responsible for generating seizures in patients with epilepsy.
- Techniques like laser ablation and stereotactic electroencephalography (SEEG) are used to identify seizure foci.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
- Stereotactic radiosurgery is often used to treat AVMs, which are abnormal tangles of blood vessels in the brain that can lead to bleeding. The radiation delivered in SRS helps shrink the AVM and reduce the risk of rupture.
- Functional Neurosurgery
- Stereotactic techniques are used in procedures like pallidotomy and thalamotomy to treat movement disorders by targeting specific brain structures responsible for abnormal motor function.
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- A painful condition that affects the trigeminal nerve. Stereotactic radiosurgery (e.g., Gamma Knife) can be used to treat this condition by precisely targeting the nerve to disrupt pain signals.
- Biopsy
- Stereotactic biopsies involve using imaging and stereotactic guidance to extract tissue samples from brain lesions for diagnostic purposes. This method minimizes risk and avoids the need for large craniotomies.
Procedure Overview:
- Preoperative Planning
Detailed imaging (MRI, CT, or PET scans) is performed to map the target area. A stereotactic frame or a frameless navigation system is used to create a reference point for the surgeon to guide their tools. - Stereotactic Frame
In some procedures, a stereotactic frame is attached to a patient’s head. This frame serves as a reference system that helps the surgeon pinpoint the exact location of the lesion or target area in three dimensions. - Surgery
Small incisions are made, and specialized instruments (e.g., biopsy needles, electrodes, or lasers) are navigated to the precise location using the stereotactic coordinate system and real-time imaging. In radiosurgery, high doses of radiation are directed at the target without any incisions. - Postoperative Care
Recovery is usually faster than with traditional surgery, or the patients typically experience less pain and fewer complications. Depending on the procedure, they may go home the same day and a after the short hospital stay.
Types of Stereotactic Surgery:
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
A non-invasive method that uses focused beams of radiation to treat brain lesions, tumors, or abnormal blood vessels.
Advantages: No incision required, high precision, minimal damage to surrounding tissues. - Stereotactic Biopsy
Involves using a needle guided by 3D coordinates to extract a small sample of tissue for diagnosis.
Advantages: Minimally invasive, high accuracy in sampling hard-to-reach brain tumors or lesions. - Stereotactic Laser Ablation
Uses laser energy to the precisely heat or a destroy abnormal tissue, often guided by MRI.
Advantages: Minimally invasive, real-time temperature monitoring to ensure precision. - Stereotactic Depth Electrode Implantation
Used in epilepsy surgery, this technique involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain to monitor seizure activity and help identify the seizure focus.
Advantages: Helps pinpoint seizure origins without large craniotomies.
Advantages of Stereotactic Surgery:
- High Precision: Allows for highly accurate targeting of brain structures and minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Minimally Invasive: Procedures typically involve small incisions or none at all, reducing recovery time, pain, and risk of infection.
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients generally experience faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery, often with shorter hospital stays.
- Versatility: Can be used for a wide range of conditions, from brain tumors and vascular malformations to epilepsy and movement disorders.
Risks and Complications:
Although stereotactic surgery is generally safer than traditional surgery, it still carries some risks:
- Infection: Any invasive procedure carries a risk of infection, though it is minimized with smaller incisions.
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding, especially in delicate brain structures.
- Damage to Nearby Structures: Despite the precision, there is a small risk of damage to nearby blood vessels, nerves, or brain tissue.
- Radiation Risks: In stereotactic radiosurgery, there is a potential risk of long-term effects from radiation exposure, although it is typically minimized with targeted delivery.
What happens before this procedure?
Medical Review:
- Your team will assess your medical history for the suitability.
- They’ll check for implanted devices, allergies, and claustrophobia.
Process Explanation:
- Your team will explain the treatment process.
- They’ll address concerns and questions to ease anxiety.
Imaging Tests:
- You’ll have CT or MRI scans to locate the tumor.
- Brain tumor patients will undergo brain MRIs.
Treatment Planning:
- Firstly, Detailed planning may include simulation.
- This simulates the treatment process before the procedure.
Dosage Determination:
- Your team will decide on radiation dosage.
- It could be a single high dose or multiple smaller doses.
Preparation of Immobilization Devices:
- Thus, Custom-fitted devices, like head frames, ensure stability.
- Once, This minimizes radiation exposure to healthy tissues.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
