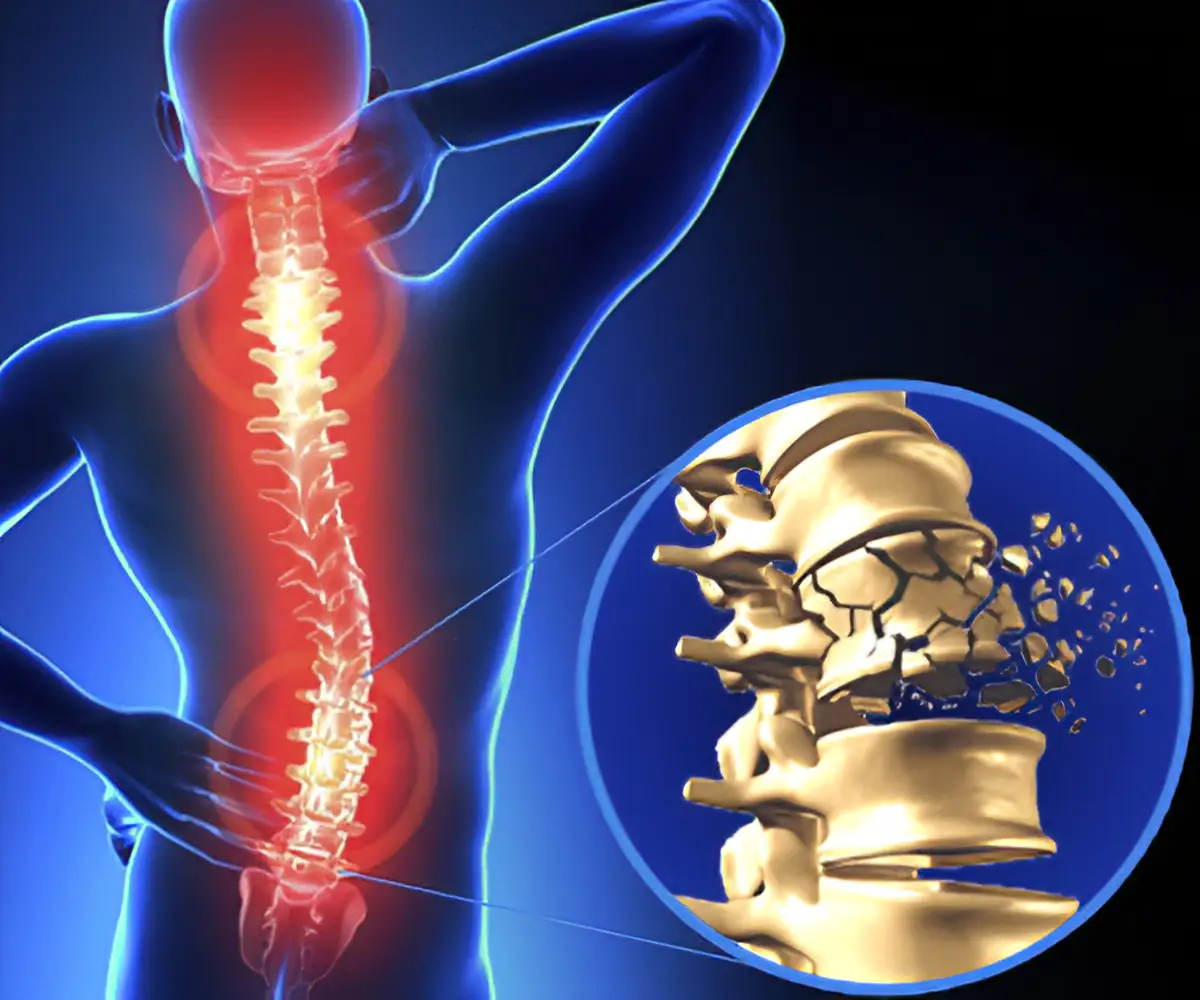
Spinal trauma
Spinal trauma in nagpur thus is an injury or damage to the spine by several agents including accidents, falls, sports injuries, violence, degenerative conditions, infections, or tumors.
Some of the key points about spinal trauma include the following:
- There are many types of spinal trauma.
- Fractures: compression, burst, flexion, extension
- Dislocations (facet joint dislocation)
- Herniated discs.
Diagnostic tests:
- X-rays
- CT scans
- MRI scans
- EMG Electromyography
Remember, any kind of spine injury needs to be attended to by a doctor as soon as possible. Call emergency or run to the hospital if you feel that someone needs medical assistance due to a spine injury.
What Is a Spinal trauma ?
Spinal trauma is a severe injury or damage caused to the spine due to various causes, including but not limited to:
- Accidents on motor vehicles, motorcycles, or from falls.
- Sports injuries.
- Due to assault or gunshot wounds.
- Degenerative conditions, such as a osteoporosis, and spinal stenosis.
- Infections, such as abscesses, or osteomyelitis, among others.
Spinal trauma can cause the following:
- Fractures/ broken bones
- Dislocation/ joints out of place
- Herniated discs- bulging or ruptured
- Spinal cord injuries (SCI)
- Nerve root injuries
Spinal trauma can therefore lead to:
These are thus the common symptoms:
– Cervical and backache
– Loss of movement
– Numbness and paresthesia
– Palsy.
Anatomy of the Spine:
The spine is composed of vertebrae, discs, spinal cord, nerves, and supporting muscles and ligaments. Trauma to any of these components can cause varying degrees of damage. Key sections of the spine include:
- Cervical spine (neck)
- Thoracic spine (mid-back)
- Lumbar spine (lower back)
- Sacral and coccygeal spine (tailbone area)
The spinal cord runs through the center of the vertebrae and transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Any damage to the spinal cord can result in severe functional loss.
Types of Spinal Trauma:
- Spinal Cord Injury (SCI): This occurs when the spinal cord is directly damaged by trauma, potentially resulting in a loss of motor, sensory, or autonomic function below the level of injury. SCIs are classified into:
- Complete SCI: Total loss of function or sensation below the injury.
- Incomplete SCI: Partial preservation of motor and sensory function below the injury level.
- Fractures of the Vertebrae: Trauma can cause vertebrae to fracture or dislocate. Some types of vertebral fractures include:
- Compression fractures: Common in the elderly and those with osteoporosis, where the front part of a vertebra collapses.
- Burst fractures: A more severe type of fracture where the vertebra shatters due to high-energy trauma, potentially compressing the spinal cord.
- Fracture-dislocations: Where a fracture and dislocation occur together, potentially causing instability and spinal cord compression.
- Herniated Discs: Trauma can cause the intervertebral discs (the cushion-like structures between the vertebrae) to rupture or bulge out, leading to nerve compression and severe pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Ligament and Muscle Injuries: Trauma can damage the ligaments and muscles that support the spine, leading to instability and difficulty in movement.
- Whiplash: A common cervical spine injury caused by a sudden acceleration and deceleration motion, such as in car accidents. It results in soft tissue damage, particularly affecting the neck muscles and ligaments.
Common Causes of Spinal Trauma:
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: The leading cause of spinal injuries, especially high-impact collisions.
- Falls: Particularly common in the elderly or construction workers, falls can cause fractures and other spinal injuries.
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports (like football, rugby, or gymnastics) and diving accidents are frequent causes of spinal trauma.
- Violence: Penetrating injuries from gunshots or knife wounds, as well as blunt trauma from physical assaults, can damage the spine and spinal cord.
- Industrial Accidents: Heavy lifting or falls in construction or manufacturing settings may result in significant spinal damage.
Symptoms of Spinal Trauma:
Symptoms vary depending on a severity or location of the injury:
- Pain: Severe pain in the neck, back, and limbs.
- Numbness or tingling: Often in the arms, legs, hands, or feet, indicating possible nerve damage.
- Weakness or paralysis: Partial or complete loss of movement in the affected limbs (quadriplegia or paraplegia depending on the injury site).
- Loss of sensation: Inability to feel touch, pain, temperature, or other sensations below the injury.
- Difficulty breathing: Cervical spine injuries can impair breathing if the diaphragm and chest muscles are affected.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: Indicative of damage to the nerves controlling the pelvic organs.
- Spinal deformity: Visible curvature or abnormal positioning of the spine.
Emergency Management:
Suggested spinal trauma, a patient should seek immediate hospital care. The principles applied to such patients include:
Immobilization of the spine : This is a method of preventing further injury due to the stabilization of the spine via a cervical collar and/or backboard or similar device.
Avoid Movement: Do not move the patient unless absolutely necessary to prevent further damage to the spinal cord by injury.
Emergency Medical Services: The patient needs to be transported immediately to the hospital as an injury could occur and should be assessed to prevent complications from arising.
Treatment of Spinal Trauma:
Treatment depends on the type or severity of the injury. Common treatment options include:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Immobilization: The use of braces, collars, or traction to stabilize the spine and prevent further injury.
- Medications:
- Steroids: High doses of corticosteroids like methylprednisolone may be administered soon after injury to reduce inflammation around the spinal cord and potentially limit damage.
- Pain relievers: To manage acute pain from fractures or disc injuries.
- Muscle relaxants: To relieve muscle spasms.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation aimed at restoring function, improving mobility, and preventing long-term complications like muscle atrophy.
2. Surgical Treatments:
Surgery is often required for more severe spinal trauma, especially if there is spinal cord compression or instability. Surgical options include:
- Spinal Decompression: To relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves by removing fragments of bone, disc material, or other structures compressing the spine.
- Spinal Fusion: Fusing two or more vertebrae together using metal rods, screws, or bone grafts to stabilize the spine and prevent abnormal motion.
- Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty: Minimally invasive procedures that involve injecting bone cement into fractured vertebrae to stabilize them and reduce pain (often used for compression fractures).
What procedures Spinal trauma?
Invasive procedures for spinal trauma include:
1. Emergency stabilization
2. Immobilization, with the use of braces, casts, and traction
3. Pain management, with the use of medication, injections
4. Diagnostic tests, for example:
* X-rays
* CT scans
* MRI scans
* EMG
5. Surgical intervention:
* Decompression: removal of the pressure from the spinal cord and nerves
* Stabilization: fusion and instrumentation
6. Rehabilitation: continuous therapy- physical therapy- occupational therapy
7. Interventional procedures:
* Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: strengthen compressed vertebrae
* Radiofrequency ablation: reduces pain
8. Minimally invasive spine surgery
9. Endoscopic spine surgery
10. Robotic spine surgery
The procedure(s) will depend on a nature or the severity of the spinal trauma or the general health of the patient. Such a patient must consult a health care professional or spine specialist for proper evaluation and planning of treatment.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
