Spinal stenosis
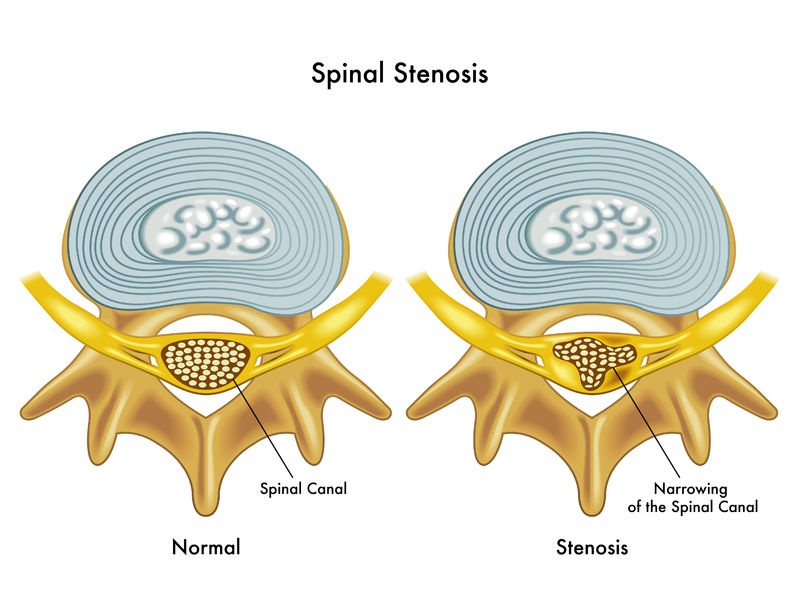
Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of spaces within the spine, which puts pressure on the nerves traveling through it. This condition can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the back, legs, and other areas of the body. Spinal stenosis is most commonly seen in adults over the age of 50 but can also result from congenital conditions, injuries, or other spinal disorders.
With the increasing prevalence of spinal disorders due to aging and sedentary lifestyles, understanding spinal stenosis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available for spinal stenosis.
Types of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is classified into two major types:
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis – Narrowing occurs in the cervical (neck) area, affecting the spinal cord and nerves leading to the arms and hands.
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis – The most common form of spinal stenosis, occurring in the lower back and affecting the nerves that travel to the legs.
Causes of Spinal Stenosis
A number of factors are responsible for the onset of spinal stenosis, such as:
- Aging – As one gets older, spinal degeneration results in ligament thickening and bone growth, reducing the size of the spinal canal.
- Osteoarthritis – Spinal joint wear and tear result in bone spur formation that pinches the nerves.
- Herniated Discs – Bulging or torn discs compress spinal nerves and cause pain and numbness.
- Congenital Spinal Stenosis – A few people are born with a naturally narrow spinal canal.
- Spinal Injuries – Injury from accidents can dislocate vertebrae and injure spinal tissues.
- Tumors – Tumors in or near the spinal canal can compress nerves.
- Thickened Ligaments – Ligaments that hold the spine together can thicken and bulge into the spinal canal.
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
Cervical Spinal Stenosis Symptoms
- Neck pain
- Weakness or numbness in arms and hands
- Difficulty balancing or walking
- Bladder or bowel dysfunction (severe cases)
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Symptoms
- Lower back pain
- Numbness or tingling in legs and feet
- Weakness in the legs
- Pain worsens with standing or walking and improves when sitting or leaning forward
Treatment Options for Spinal Stenosis
Non-Surgical Treatments
1.Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including ibuprofen and naproxen inhibit inflammation and pain.
- Muscle relaxants alleviate muscle spasms.
- Corticosteroid injections temporarily relieve inflammation.
2.Physical Therapy
- Spinal support is enhanced by strengthening and stretching exercises.
- Spinal strain is minimized by posture correction techniques.
- Helpful Devices
- Mobility is enhanced through walking aids like canes or braces.
3.Alternative Therapies
- Chiropractic manipulations, acupuncture, and massage relieve pain in some patients.
Surgical Treatments
- Laminectomy – Removal of the lamina (rear portion of the vertebra) to make room in the spinal canal.
- Spinal Fusion – Fusion of two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
- Foraminotomy – Widening of nerve passageways to decrease pressure on spinal nerves.
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) – Small incisions and specialized instruments decrease recovery time and complications..
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-treatment rehabilitation is essential for recovery. This includes:
- Gradual return to activities
- Continued physical therapy and stretching exercises
- Regular follow-ups with the doctor
Preventing Spinal Stenosis
Although spinal stenosis tends to be age-related, certain precautions can limit its effects:
- Maintain an optimal weight to avoid putting undue pressure on the spine.
- Regular exercise, such as core-strengthening exercises, can help.
- Sit and stand correctly, with good posture.
- Minimize heavy lifting that can cause harm to spinal discs.
- Hydrate regularly to keep discs flexible.Contact Us
Conclusion
Spinal stenosis is a common yet manageable condition that affects many individuals, especially as they age. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve quality of life and prevent severe complications. Whether through conservative methods like physical therapy and medications or surgical interventions, patients can find relief and restore their mobility.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
