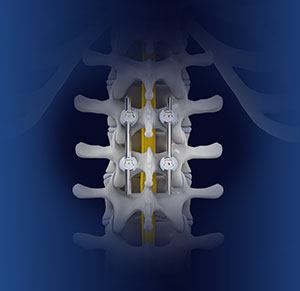
Spinal fusion
The medical condition in which spinal fusion in nagpur is the surgery that connects two more bones of any part of the spine, such that the prevention of movement between them takes place and helps prevent pain.
Spinal fusion is a surgical operation that involves joining of two or more vertebrae in the spine to stabilize and strengthen the spine. It serves for:
- Prevents movement between vertebrae
- To ease the pain and discomfort
- Spinal alignment is improved
- Bring back stability.
What Is a Spinal fusion?
A spinal fusion is the surgical process of bonding two or more vertebrae in the spine to a solid bone mass. It is done to achieve:
– Spinal stabilization
– Pain relief
– Re-establishment of correct spine alignment
– Stability
In this surgical procedure:
– Bone grafting or substitutes are applied to encourage fusion.
– Instruments, which may include rods or screws or cages, may be used to afford some stabilization.
– Vertebrae are fused to form a solid bone mass.
Some of the conditions treated with spinal fusion include the following:
Degenerative disc disease
Scoliosis
Spondylolisthesis
Spinal fractures
Herniated discs
For a consultation with a healthcare professional to decide if you should have spinal fusion, end.
When is Spinal Fusion Recommended?
Spinal fusion is typically performed for a variety of conditions that cause instability, pain, or deformity in the spine, including:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related changes in the spinal discs can lead to instability and chronic pain.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal curvature of the spine may require fusion to prevent further curvature and pain.
- Spondylolisthesis: A condition in which one vertebra slips forward over another, causing instability.
- Herniated Disc: Sometimes, spinal fusion is done after a discectomy (removal of a herniated disc) if the spine is unstable.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal that compresses the spinal cord and nerves, often treated with fusion to prevent further compression.
- Spinal Fractures: Caused by trauma or conditions like osteoporosis, fractures may require fusion to stabilize the spine.
- Infections or Tumors: In rare cases, spinal fusion is done to stabilize the spine after infection or tumor removal.
Types of Spinal Fusion:
There are different techniques used in spinal fusion surgery, depending on the specific condition and area of the spine affected:
- Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF): Fusion of the vertebrae from the front (anterior) of the spine.
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF): Fusion from the back (posterior) of a spine.
- Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): A variation of PLIF, this technique fuses the spine from the back and side (transforaminal) approach.
- Cervical Fusion: Fusion in the neck area (cervical spine), often used for conditions like herniated discs in the neck.
- Minimally Invasive Spinal Fusion: Some fusion surgeries can be done using smaller incisions and specialized tools, leading to quicker recovery and less tissue damage.
How Spinal Fusion is Performed:
- Bone Grafts: During spinal fusion, bone grafts (either from the patient or a donor) or artificial bone substitutes are placed between the vertebrae to encourage them to grow together and fuse. These grafts act as a scaffold for new bone growth.
– Autograft: Bone taken from another part of the patient’s body, typically the pelvis.
– Allograft: Bone taken from a donor.
– Bone substitutes: Synthetic materials that promote bone growth. - Fixation Devices: To keep the vertebrae stable while the bones fuse, surgeons often use metal rods, screws, and plates.
Risks of Spinal Fusion:
Like all surgeries, spinal fusion has some risks, including:
- Infection: Risk of infection at a surgical site.
- Bleeding: Blood loss during the procedure.
- Nerve Damage: Potential for nerve injury, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Blood Clots: Risk of blood clots forming in a legs (deep vein thrombosis).
- Failure to Fuse: Sometimes, the vertebrae do not fuse as expected, requiring additional surgery.
- Adjacent Segment Disease: Fusion may increase stress on adjacent spinal segments, leading to degeneration over time.
Recovery from Spinal Fusion:
Recovery from spinal fusion can take several months. Key aspects of recovery include:
- Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in a hospital for 2-4 days after surgery.
- Pain Management: Pain is managed with medications, and most patients experience significant improvement in pain once the fusion heals.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often required to regain strength, flexibility, or mobility after surgery.
- Activity Restrictions: During the initial weeks of recovery, patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, bending, twisting, or other activities that can strain the spine.
- Bone Healing: Full fusion and bone healing typically take 6-12 months. During this time, patients will have regular follow-up visits with their surgeon to monitor progress.
Alternatives to Spinal Fusion:
Spinal fusion is considered when other, less invasive treatments are not effective. These alternatives may include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises or stretches to strengthen muscles around the spine.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatories, pain relievers, and muscle relaxants.
- Spinal Injections: Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Discectomy or Laminectomy: In some cases, removing part of a disc or vertebrae without fusion may be enough to relieve symptoms.
- Artificial Disc Replacement: An alternative to spinal fusion for some patients, preserving mobility by replacing a damaged disc with an artificial one.
What procedures Spinal fusion?
The type of spinal fusion procedure done might depend on the nature of the condition that is being treated and the location. Some of the widely performed procedures are as follows:
1. Posterolateral Fusion (PLF): This is one of the most common types of spinal fusion procedures. Posterolateral fusion was mainly associated with the spinal region of the lumbar area and the use of bone graft along with instrumentation like rods and screws.
2. Interbody Fusion (IBF): Interbody fusion is another common procedure for spinal fusion. In interbody fusion, the vertebral column in the neck region or the lower back is connected using a bone graft assisted by instrumentation.
3. ALIF-Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Vertebra fusion in the low back accessed from the anterior side by a bone graft and instrumentation
4. TLIF-Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Vertebra fusion in the low back accessed from the lateral side with a bone graft and instrumentation.
5. Lateral Interbody Fusion (LIF): Fusion of the vertebrae of the lower back approaching the side (lateral) with a bone graft and instrumentation.
6. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion (OLIF): Fusion of the vertebrae of the lower back approaching an oblique angle with a bone graft and instrumentation.
7. Cervical Fusion: Fusion of the vertebrae of the neck with a bone graft and instrumentation.
8. Minimally Invasive Spinal Fusion This is a procedure where smaller incisions and instruments are used attempting to avoid any kind of soft tissue damage as much as possible. However, this decision would be made by your surgeon about which type of procedure suits you and your condition better.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
