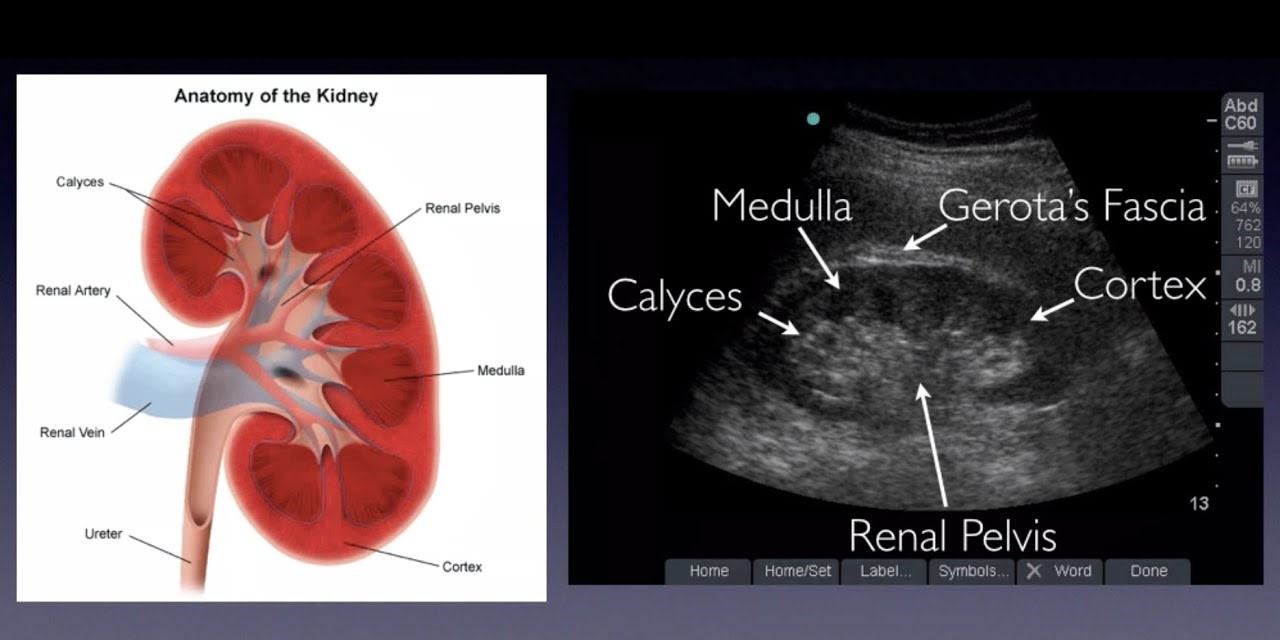
Renal ultrasound
The term renal ultrasound in Nagpur is commonly known as kidney ultrasound, which is essentially an ultrasonic imaging of the kidney system. It is a non-invasive test, based on high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the kidneys and tissues. It can help in diagnosing and monitoring different conditions related to the kidney, such as:-
1. Kidney stones
2. Kidney cysts or masses
3. Renal inflammation or infection (pyelonephritis)
4. Kidney damage, or scarring
5. Kidney tumors (benign or malignant)
Renal ultrasound provides the following information:
1. Size and Shape of the Kidney
2. Location and Position of the Kidney
3. Texture and Echogenicity of the Kidney
4. Kidney Stones, Cysts, and Masses
5. Pyelonephritis (Kidney Inflammation)
6. Kidney Damage and Scarring
7. Benign and Malignant Tumors in the Kidneys
8. Hydronephrosis: Fluid Accumulation in the Kidneys
9. Renal Artery Stenosis and Narrowing of the Renal Artery
10. Blood Flow and Perfusion of the Kidneys
11. Thickness of the Cortical and Medullary Regions of the Kidneys
12. Perinephric fluid or hemorrhage
Renal ultrasound is used for purposes such as:
1. Evaluation of the functioning and anatomy of the kidneys
2. Diagnosis of diseases or abnormalities of the kidneys
3. Biopsies or other interventional procedures
4. Monitoring patients who have undergone kidney transplants
5. Patients with high risk of a developing kidney-related issues
6. Following the extent of kidney damage following injury or trauma
7. Monitoring the size and function of chronic kidney patients
8. Diagnosing kidney tumors or cysts
9. Kidney blood flow and perfusion
10. Support renal artery stenting or any other vascular intervention
What Is a Renal ultrasound ?
A renal ultrasound, another name for a kidney ultrasound, is an non-invasive and non-radiation test for medical imaging. High-frequency sound waves produce images of the kidneys and the surrounding tissues.
While undergoing a renal ultrasound, the probe known as a transducer is placed on a abdomen over the area of the kidney. Sound waves that are sent and received produce images of the kidneys and adjacent tissues on a monitor.
Indications for renal ultrasound include:
– Evaluation of anatomy and function of the kidney.
– Disease and abnormalities in the kidney.
– Biopsies or other interventional procedures.
– Monitoring of patients who have received a kidney transplant.
– Screening of the kidney for problems in high-risk patients.
For any healthcare provider, renal ultrasound is useful for the following purposes:
– The process assesses the size and shape of the kidneys
– It detects kidney stones, cysts, or masses
– It evaluates a blood flow or a perfusion through a kidneys
– For the detection of inflammation or infection within the kidneys
– Checks whether there is any scarring or injury of the kidneys
– Kidney artery stenting or vascular interventions are guides.
Reasons for a Renal Ultrasound:
- Kidney stones: To detect the presence of stones in the kidneys or urinary tract.
- Kidney infections: To evaluate for conditions like pyelonephritis or abscesses.
- Cysts or tumors: To identify abnormal growths in the kidneys or surrounding areas.
- Hydronephrosis: To check for swelling or blockage in the kidneys due to fluid buildup.
- Congenital abnormalities: Especially in children, to identify any structural abnormalities from birth.
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD): To monitor progression or assess damage to the kidneys.
- Urinary retention: To evaluate how well the bladder is functioning in holding and releasing urine.
What is procedures of Renal ultrasound ?
Steps involved in renal ultrasound procedures are given below:
1. Preparation
– There is no the special preparation for this procedure
– Wear loose-fitting, comfortable clothing that lets you expose the abdomen
2. Positioning
– Lie on your back and your side with the abdomen exposed
– A pillow or pad may be placed under your back for the support
3. Placement of a transducer
– A small probe or transducer is placed on your abdomen.
– Image improvement with gel and a oil on the skin
4. Scanning
– The transducer sends or receives ultrasound waves to display images on a monitor
5. Doppler study
– Checks the movement of blood within the kidneys and other tissues next to it
6. Image interpretation
– Images and measurements are studied by the sonographer or the radiologist
7. Reporting:
-Proven report outlining findings and recommendations
8. Additional intervention:
-Cytic aspiration via fine-needle biopsy
-Stenting of the renal artery and any other form of vascular intervention
9. Post-procedure
– You can resume normal activities and return home immediately after
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
