Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain in Nagpur is pain or aching in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or genital area. It might be acute or chronic, or its severity may vary from mild to severe.
Common causes of pelvic pain are:
1. Menstruation (cramps, dysmenorrhea)
2. Endometriosis
3. Adenomyosis
4. Fibroids
5. Ovarian cysts or torsion
Symptoms of Pelvic pain include:
- Sharp stabbing or dull pain
- Cramping, aching, or heaviness
- Pain during sex or during bowel movements
- Dyspareunia/painful urination
- Abnormal bleeding and spotting
- Abdominal tenderness or swelling
Diagnosis
- Medical history and physical exam
- Pelvic exam
- Ultrasound and imaging tests (CT, MRI scans)
- Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy
- Blood tests example, pregnancy and infection.
Treatment
- Pain management with analgesics, heat and cold therapy
- Hormonal therapies example, birth control and hormone replacement
- Some of the treatments that are advised in such conditions include;
- Use of antibiotics if the patient is infected
- Surgical procedure especially, laparoscopy or hysterectomy
- Physical therapy to overcome pelvic floor dysfunction
- Alternative therapies including acupuncture and massage
If you are suffering from pelvic pain, see a professional health provider for diagnosis and treatment.
What Is a Pelvic pain?
Pelvic pain is an ache or pain in the pelvic or genital area or the lower abdomen. The experience can be sharp and stabbing or dull and aching. Pelvic pain can be acute, which lasts from hours to weeks, or chronic, lasting months or years.
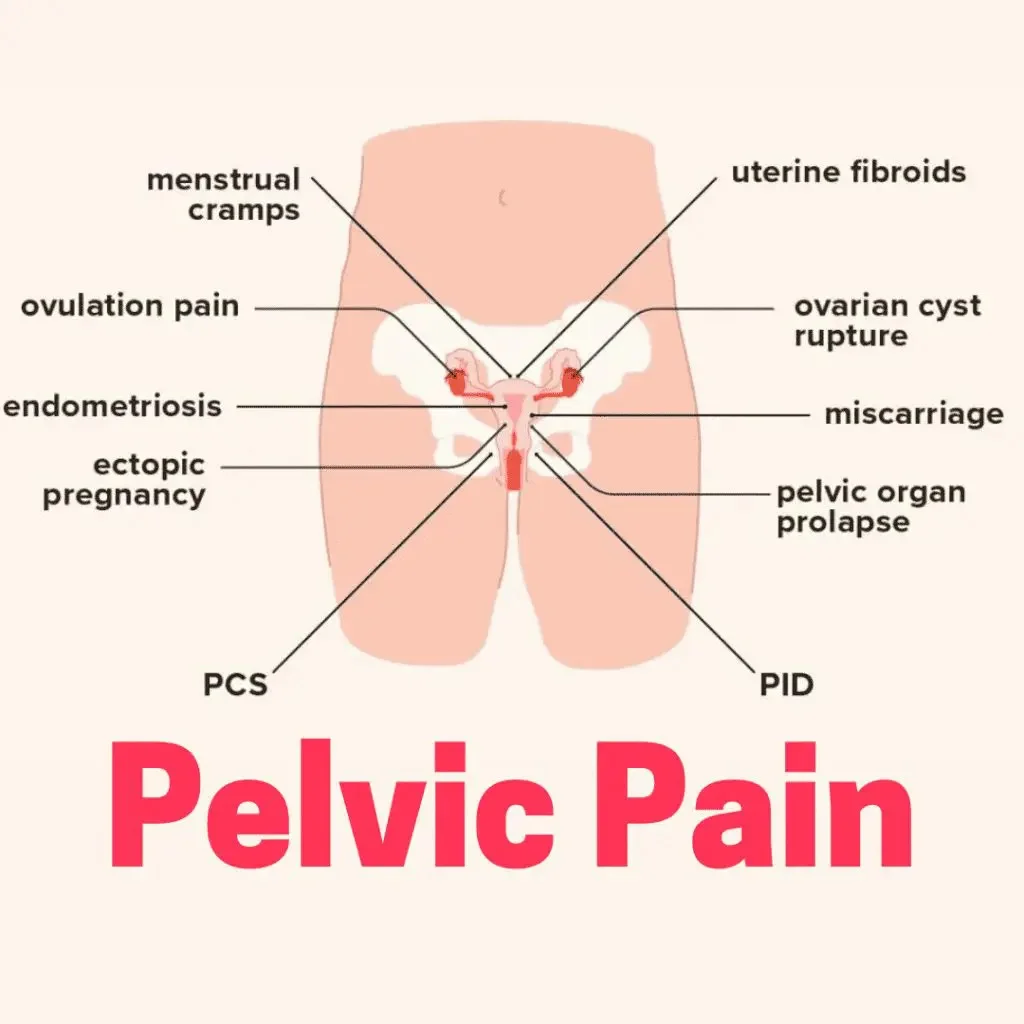
Several sources of pelvic pain can be cited, including, but not limited to:
Reproductive organs: uterus, ovaries, cervix, vagina
Musculoskeletal structures: pelvic floor muscles, ligaments, joints
-Gastrointestinal tract (bowel, bladder)
– Urinary tract
– Nerves (pudendal nerve, sciatic nerve)
Pelvic pain can also be classified into other groups, for instance:
Dysmenorrhea (cramping)
Vulvodynia: any vulvar pain
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Endometriosis
Adenomyosis
Fibroids
Ovarian cyst or torsion
Pelvic pain impacts daily life, creating discomfort, inconvenience, and low ability to perform day-to-day activities. Whether you experience pelvic pain, you need to seek your health care provider for an evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain can originate from various structures in the pelvic region, including the reproductive organs, urinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and musculoskeletal system. Common causes include:
- Reproductive System Issues:
- Menstrual Cramps: Pain associated with menstruation (dysmenorrhea).
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing pain or inflammation.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries that can cause pain if they rupture or become large.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): An infection of the female reproductive organs that can cause pain and other symptoms.
- Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus that can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding and pain.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube, which can cause severe pain and is a medical emergency.
- Urinary System Issues:
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Infections in the bladder or urethra can cause pelvic pain, especially during urination.
- Interstitial Cystitis: A chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain, or pelvic pain.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits that form in the kidneys can cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract.
- Gastrointestinal Issues:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional gastrointestinal disorder that can cause abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix, which can cause severe abdominal and pelvic pain.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation and infection of pouches in the colon that can lead to pelvic discomfort.
- Musculoskeletal Issues:
- Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: Weakness or tightness in the pelvic floor muscles can cause pain during activities or intercourse.
- Hernias: An inguinal and femoral hernia can cause pelvic pain, especially when straining.
- Other Causes:
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can contribute to chronic pelvic pain.
- Pelvic Congestion Syndrome: Chronic pelvic pain caused by varicose veins in the pelvic region.
Symptoms
Pelvic pain can present in various ways, depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or dull ache in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Pain during menstrual periods (dysmenorrhea)
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Abnormal menstrual bleeding
- Urinary symptoms (burning, urgency, frequency)
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (bloating, changes in bowel habits)
Diagnosis
Diagnosing the cause of pelvic pain involves a thorough evaluation, including:
- Medical History: Discussing symptoms, medical history, and any relevant lifestyle factors.
- Physical Exam: A pelvic examination to assess reproductive organs and identify any abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, urine tests, or cultures to identify infections or hormonal issues.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the pelvic organs and identify structural issues like cysts, fibroids, or tumors.
Treatment Options
Treatment for pelvic pain depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Medications:
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs) can be a help of alleviate discomfort.
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or other hormonal treatments may be prescribed for conditions like endometriosis or fibroids.
- Antibiotics: For infections like UTIs or PID.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments: Modifying diet to manage symptoms of IBS or interstitial cystitis.
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening pelvic floor muscles and improving overall health.
- Physical Therapy: Pelvic floor therapy can help address muscle dysfunction and alleviate pain.
- Surgical Options: In cases of severe conditions (e.g., large fibroids, ectopic pregnancy), surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Psychological Support: Counseling or therapy may help address emotional and psychological factors contributing to chronic pelvic pain.
What is procedures Pelvic pain?
Its management procedures include the following:
1. Diagnostic laparoscopy: This is a minimum surgical procedure that involves seeing the pelvic organs.
2. Hysteroscopy: It is looking inside the uterus using a narrow scope attached to a camera.
3. Endometrial ablation: It is a process of decreasing or entirely stopping menstrual flow.
4. Radiofrequency ablation: This is a minimum surgical procedure directed towards treating fibroids or adenomyosis.
5. Pelvic floor physical therapy: It involves specific exercise plans to relax the muscles in the pelvic floor.
– Medications
Trigger point injections: Injection with local anesthetics or steroids into painful areas
– Nerve blocks: injection of local anesthetics or steroids to block pain around nerves
– Surgery for endometriosis: fibroids, or adenomyosis.
– Hysterectomy: removal of uterus through surgery
– Pelvic floor reconstruction: surgical procedures meant to repair or reconstruct pelvic floor muscles and tissues
6. Pain management procedures:
-Nerve ablation
-Spinal cord stimulation
-Pain pumps
7. Alternative therapies
-Acupuncture
-Massage
-Chiropractic care.
– Yoga and physiotherapy
These treatments can do the proper diagnosis of a condition and either remove the causes of pain or treat them to improve quality of life and reduce discomfort. Consult with a health care provider for what treatment is needed for your specific case.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
