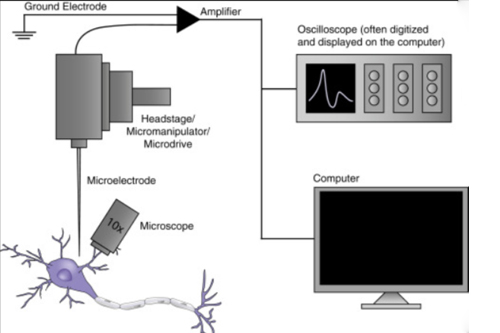
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (EP) in Nagpur is a specialized cardiac study that examines the heart’s electrical activity in detail. This advanced procedure is essential in diagnosing and treating irregular heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias.
During an EP study, cardiologists use cardiac catheters—small, flexible tubes—along with sophisticated computer systems to record electrical signals directly from within the heart. Unlike traditional electrocardiograms (EKGs) that rely on external electrodes, this method provides highly precise measurements using sensors placed inside the heart, offering critical insights that external tests cannot capture.
What is Electrophysiology?
Electrophysiology is a branch of science that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It focuses on understanding how cells generate and respond to electrical signals, which are essential for processes like nerve impulses, muscle contractions, and heartbeats. This field combines principles from physics, biology, and engineering to explore the electrical activity that underpins life itself.
From diagnosing heart arrhythmias to uncovering the mysteries of brain function, electrophysiology plays a critical role in both medical and research settings. Techniques like patch clamping and extracellular recording allow scientists to measure tiny electrical currents in cells, providing insights into how diseases disrupt normal function and how treatments can restore it.
The importance of electrophysiology cannot be overstated. In cardiology, it helps doctors diagnose and treat irregular heart rhythms. In neuroscience, it enables researchers to map brain activity and understand disorders like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease. Beyond medicine, electrophysiology is also used in drug development, where it helps test the safety and efficacy of new medications.
As technology advances, electrophysiology continues to evolve. Innovations like optogenetics, which uses light to control cells, and AI-driven data analysis are pushing the boundaries of what we can achieve. Whether you’re a medical professional, a researcher, or simply curious about how your body works, electrophysiology offers a fascinating glimpse into the electrical symphony that keeps us alive.
How Electrophysiology Works
1. Basic Principles of Electrical Activity in Cells
- Sodium (Na⁺)
- Potassium (K⁺)
- Calcium (Ca²⁺)
- Chloride (Cl⁻)
The cell membrane acts as a barrier, and specialized proteins called ion channels regulate the flow of these ions. When ion channels open or close, they allow ions to move in or out of the cell, creating electrical currents. These currents can change the membrane potential, leading to electrical signals like action potentials in neurons or pacemaker activity in heart cells.
2. Role of Ions and Membrane Potentials
- Sodium-Potassium Pump (Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase): This pump actively transports 3 Na⁺ ions out of the cell and 2 K⁺ ions into the cell, using energy from ATP.
- Selective Permeability: The cell membrane is more permeable to K⁺ than Na⁺ at rest, allowing K⁺ to leak out and maintain the negative charge.
When a cell is stimulated, ion channels open, allowing Na⁺ to rush in and depolarize the membrane (make it less negative). If the depolarization reaches a threshold, it triggers an action potential, a rapid spike in voltage that propagates along the cell membrane. After the action potential, the cell repolarizes by allowing K⁺ to leave, restoring the resting potential.
Applications of Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology is a versatile field with applications spanning medicine, research, and technology. By studying the electrical activity of cells and tissues, electrophysiology provides critical insights into how the body functions and how diseases disrupt these processes.
1. Electrophysiology in Neuroscience
2. Electrophysiology in Cardiology
3. Electrophysiology in Drug Development
4. Electrophysiology in Cellular Biology
5. Electrophysiology in Clinical Diagnostics
6. Electrophysiology in Research and Academia
7. Emerging Applications of Electrophysiology
Types of Electrophysiological Studies
Electrophysiological studies are diverse and can be categorized based on the techniques used, the scale of investigation, and the context in which they are applied. These studies are essential for understanding the electrical properties of cells and tissues, and they play a critical role in both research and clinical settings.
1. Intracellular vs. Extracellular Recording
- Resting Membrane Potential: The baseline electrical charge of a cell.
- Action Potentials: Rapid changes in membrane potential that transmit signals in excitable cells like neurons and muscle cells.
- Synaptic Potentials: Electrical changes caused by neurotransmitter release at synapses.
- Extracellular recording measures electrical activity outside the cell, often using electrodes placed near a group of cells. This technique is commonly used to study:
- Neural Activity: Recording from neurons in the brain or spinal cord.
- Cardiac Activity: Monitoring heart rhythms using surface electrodes (e.g., ECG).
2. In Vitro vs. In Vivo Studies
- Patch Clamp Experiments: Studying ion channels in isolated cells.
- Brain Slice Recordings: Investigating neural circuits in thin slices of brain tissue.
- In vivo studies are conducted in living organisms, providing a more comprehensive understanding of physiological processes. Examples include:
- EEG Recordings: Measuring brain activity in humans or animals.
- Cardiac Electrophysiology Studies: Mapping heart rhythms in patients with arrhythmias.
3. Clinical vs. Research Applications
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Diagnosing heart conditions like arrhythmias or heart attacks.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Monitoring brain activity in patients with epilepsy or sleep disorders.
- Electromyogram (EMG): Assessing muscle and nerve function in neuromuscular disorders.
-
- Studying Ion Channels: Investigating the properties and functions of ion channels in health and disease.
- Mapping Neural Circuits: Understanding how neurons communicate and form networks.
- Developing New Therapies: Testing the effects of drugs or treatments on cellular electrical activity.
4. Single-Cell vs. Network-Level Studies
- Patch Clamp Recording: Measuring ion channel activity in a single cell.
- Intracellular Recording: Studying action potentials or synaptic potentials in individual neurons.
-
- Multi-Electrode Arrays (MEAs): Recording from multiple cells simultaneously.
- EEG or ECG: Measuring activity across large areas of the brain or heart.
5. Emerging Techniques in Electrophysiology
- Optogenetics: Using light to control ion channels in genetically modified cells.
- Voltage Imaging: Visualizing electrical activity using fluorescent dyes.
- High-Density Electrode Arrays: Recording from thousands of cells simultaneously.Contact Us
Conclusion
Electrophysiological studies are diverse and adaptable, making them invaluable for understanding the electrical properties of cells and tissues. Whether conducted in a lab or a clinic, on single cells or entire networks, these studies provide critical insights into how the body functions and how diseases disrupt these processes. As technology continues to evolve, electrophysiology will remain at the forefront of biological and medical research.Schedule your Consultation with Dr. Ritesh Nawkhare
