Disc replacement
Disc replacement in nagpur is a surgical procedure wherein an artificial disc implant replaces the diseased or injured spinal disc. The sole objective of this procedure is to restore natural motion or function for a healthy spine. By doing so, pain and discomfort are taken away.
Disc replacement surgery relieves several benefits, such as:
- Pain or pressure on the spine and nerves
- Restore the normal mobility of the spine
- Overall Quality of Life
However, it is still of paramount importance that one should first consult a doctor to determine whether or not the surgery is recommended for your particular case.
Disc replacement surgery can be performed in various spine regions, including:
1. Cervical (neck)
2. Thoracic (mid-back)
3. Lumbar (lower back)
What Is a Disc replacement ?
This is a surgical procedure where the damaged or diseased spinal disc is replaced by an artificial disc implant engineered to mimic the function and motion of a healthy natural disc. This is done with materials like metal or plastic and aims to achieve the following results during the spine’s replacement:
1. Height preservation and stabilization
2. Natural motion and flexibility
3. Reduction of strain on adjacent nerves and the spine
Disc replacement is indicated as a treatment for conditions such as
1. Herniated discs
2. Degenerative disc disease
3. Disc degeneration
4. Spinal stenosis
5. Spondylosis
Goals of disc replacement are:
Pain and discomfort relief
Reestablishment of natural motion or the function of the spine
Better quality of life.
Disc replacement is normally done in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar regions of the spine. If you are interested in disc replacement, discuss the decision with your health practitioner as soon as possible to determine whether or not disc replacement surgery is a viable course of treatment for your condition.
Purpose of Disc Replacement:
The goal of a disc replacement surgery is to:
- Relieve pain caused by a damaged disc that is compressing spinal nerves or the spinal cord.
- Restore normal movement between the vertebrae.
- Preserve spinal flexibility and motion, unlike spinal fusion, which permanently locks the vertebrae together.
Conditions Treated by Disc Replacement:
Disc replacement is a typically recommended for patients with:
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD): Age-related degeneration of the intervertebral discs, leading to pain or limited mobility.
- Herniated Disc: When the inner gel-like material of the disc leaks out and presses on nearby nerves.
- Radiculopathy: Nerve pain radiating down the arms (in cervical disc disease) or legs (in lumbar disc disease) due to nerve compression.
- Non-Responsive to Conservative Treatment: Candidates for disc replacement surgery are usually those who have not found relief from physical therapy,
- medications, injections, or other non-surgical treatments.
Types of Disc Replacement:
There are two main types of disc replacement surgeries based on the location in the spine:
- Cervical Disc Replacement (in the neck):
– Used to treat degenerative disc disease or herniated discs in the cervical spine.
– Surgeons access the spine from the front of the neck (anterior approach) to remove the damaged disc and replace it with an artificial disc.
– Cervical disc replacement is often performed instead of spinal fusion to preserve neck motion. - Lumbar Disc Replacement (in the lower back):
– Used to treat disc-related issues in the lumbar spine.
– Surgeons access the spine from the front of the abdomen (anterior approach), remove the damaged disc, or insert an artificial disc.
– Lumbar disc replacement is less common than cervical disc replacement, and it is usually considered for younger patients without significant spinal degeneration.
Types of Artificial Discs:
There are different types of artificial discs designed to mimic the natural motion of the spine. These discs are typically made from materials like metal, plastic, or a combination of both. Some artificial discs allow for a range of motions, including:
- Flexion/Extension: Bending forward and backward.
- Lateral Bending: Bending from side to side.
- Axial Rotation: Twisting movements.
The specific type of disc used depends on the patient’s anatomy and the surgeon’s preference.
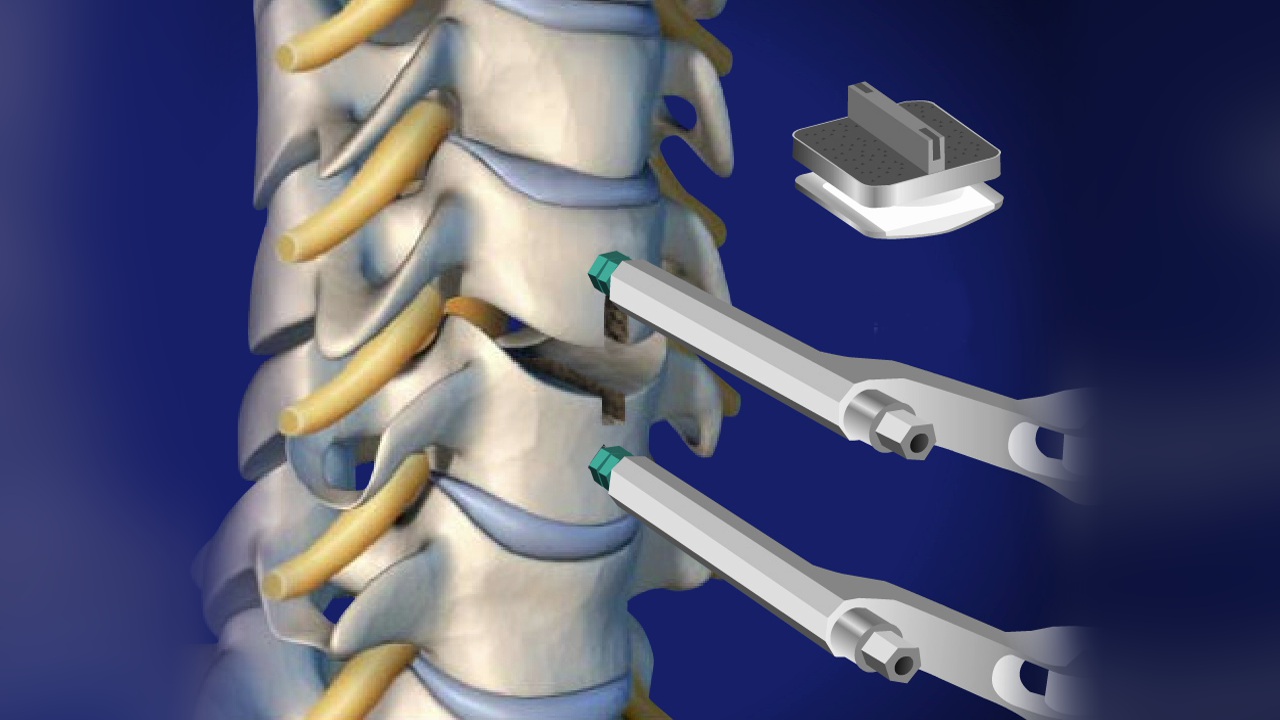
Procedure for Disc Replacement Surgery:
- Anesthesia: Disc replacement is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is unconscious during the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision, usually at the front of the neck for cervical disc replacement or the front of the abdomen for lumbar disc replacement.
- Disc Removal: The damaged or degenerated disc is carefully removed, creating space between the affected vertebrae.
- Artificial Disc Insertion: The artificial disc is placed in the space where the natural disc was removed. The device is positioned to allow normal movement between the vertebrae.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures, or the patient is taken to recovery.
Recovery After Disc Replacement Surgery:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for 1-3 days, depending on the type and complexity of the surgery.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation typically begins a few weeks after surgery, with exercises designed to restore strength, mobility, and flexibility.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are the advised to a avoid heavy lifting, bending, or twisting for several weeks. Light activities, like walking, are encouraged to promote healing.
- Pain Management: Pain following surgery is managed with medications, including NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or opioids for short-term use.
- Return to Work: Most patients can return to light work within a few weeks, but physically demanding jobs may require a longer recovery period.
Risks and Complications of Disc Replacement:
As with any surgery, disc replacement carries certain risks, including:
- Infection: Though rare, infection can occur at the surgical site.
- Implant Failure: The artificial disc may fail or wear out over time, requiring revision surgery.
- Nerve Damage: There’s a small risk of damage to the nerves or spinal cord during the procedure, leading to weakness, numbness, or paralysis.
- Blood Vessel Injury: Since the spine is accessed from the front, there is a risk of injury to blood vessels in the neck or abdomen.
- Adjacent Segment Degeneration: While less common than with fusion, adjacent segments of the spine can still degenerate over time, potentially leading to additional issues.
Alternatives to Disc Replacement:
- Spinal Fusion: Involves removing the damaged disc and permanently joining the vertebrae together to eliminate motion at the affected segment.
- Conservative Treatments: Before surgery, doctors may recommend physical therapy, medications, steroid injections, or other non-invasive treatments.
- Microdiscectomy: A minimally invasive surgery to remove part of a herniated disc, typically used for smaller disc problems.
What procedures Disc replacement ?
Disc replacement procedures include:
1. Total disc replacement (TDR). The entire disc is replaced by an artificial one.
2. Partial disc replacement. In this the disc is partially replaced, in case the affected portion of the disc only.
3. Disc arthroplasty. An implant will be used in place of the disc so that it does mimic the function of the natural disc.
4. Artificial disc insertion: Artificial disc is inserted directly into the disc space.
5. Disc replacement and fusion. Disc replacement is combined with spinal fusion to fixate the spine.
6. Minimally Invasive Disc Replacement: Gives smaller incisions and particular instruments to reduce tissue damage.
7. Cervical Disc Replacement: Replaces the discs in the cervical spine or neck.
8. Lumbar Disc Replacement: Replaces the discs in the lower back or lumbosacral.
9. Thoracic Disc Replacement: Replaces discs in the mid-back or thoracic.
These surgeries can be done using various techniques, such as:
1. Open Surgery
2. Minimally invasive surgery
3. Endoscopic Spine Surgery
4. Robotic Spine Surgery
The course and treatment are somewhat variable to patient condition, region of the spine, and surgeon preference.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
