Degenerative disc disease
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is common spinal condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs due to the gradual wear and tear of the intervertebral discs, leading to pain, reduced mobility, and discomfort. Although it is a natural part of aging, DDD can be accelerated by lifestyle factors, injuries, and genetic predisposition.
In Nagpur, an increasing number of individuals are seeking medical treatment for degenerative disc disease due to sedentary lifestyles, poor posture, and the rising prevalence of obesity. Fortunately, the city is home to some of the best spine specialists, orthopedic doctors, and neurosurgeons offering cutting-edge treatment options for DDD.
What Is a Degenerative disc disease?
DDD is not actually a disease but a term used to describe age-related changes in spinal discs. These discs act as cushions between vertebrae, providing flexibility and shock absorption. Over time, these discs lose their hydration and elasticity, leading to pain and other complications.
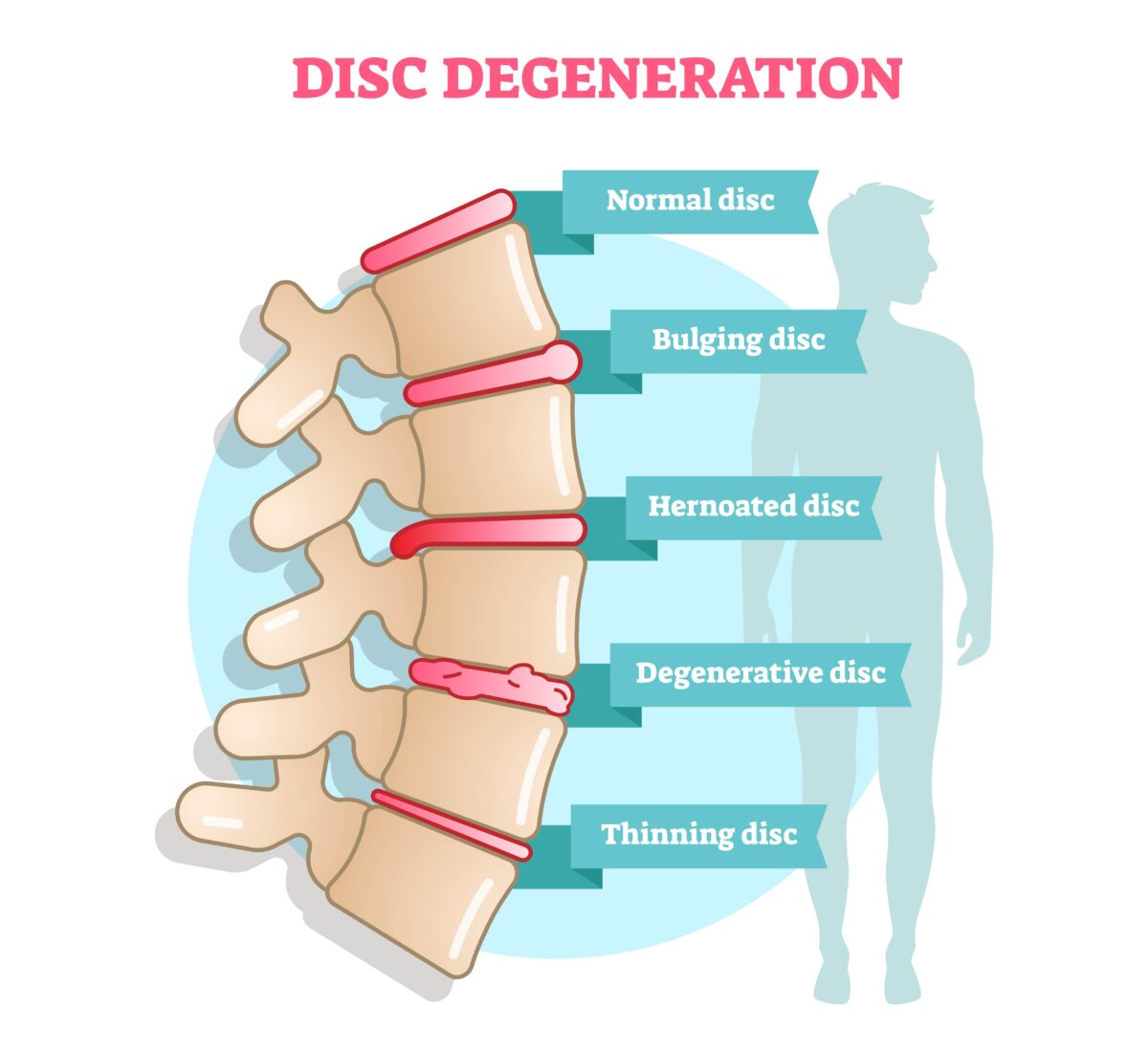
Stages of Degenerative Disc Disease
- Initial Disc Dehydration – Loss of fluid content, leading to reduced disc height.
- Disc Bulging and Weakness – The disc weakens, causing bulging or minor herniation.
- Disc Collapse – Further degeneration leads to reduced space between vertebrae.
- Bone Spurs Formation – The body forms osteophytes (bone spurs) to stabilize the spine, which can press on nerves, causing pain.
Common Causes of DDD
- Aging – The most common cause, as discs naturally degenerate over time.
- Genetics – A family history of spinal disorders increases the risk.
- Injury or Trauma – Accidents or repetitive strain accelerate disc degeneration.
- Obesity – Excess weight puts additional stress on spine.
- Poor Posture – Prolonged sitting and improper lifting techniques strain the spine.
- Smoking – Reduces blood flow to discs, affecting their ability to repair and regenerate.
Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease
- Chronic back or neck pain – Typically worsens with movement and improves with rest.
- Stiffness and reduced flexibility – Difficulty in bending or twisting.
- Pain radiating to arms or legs – If nerve compression occurs, pain may extend to the extremities.
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness – Compression of spinal nerves can lead to neurological symptoms.
- Muscle spasms – Involuntary tightening of muscles around the spine.
Diagnosing Degenerative Disc Disease in Nagpur
- X-rays – Help detect disc height loss and bone spurs.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – Provides detailed images of spinal discs, nerves, and soft tissues.
- CT Scan – Useful for detecting structural abnormalities.
- Discography – Involves injecting contrast dye into discs to identify painful areas.
Treatment Options for Degenerative Disc Disease:
Treatment for DDD varies depending on the severity of the condition. The goal is to relieve pain, improve mobility, and prevent further degeneration.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Pain Relievers – Over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin) reduce inflammation and pain.
- Muscle Relaxants – Help relieve muscle spasms.
- Steroid Injections – Corticosteroid injections provide temporary relief from severe pain.
- Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing DDD. A trained physiotherapist can recommend:
- Strengthening exercises to support the spine.
- Stretching techniques to improve flexibility.
- Postural correction to reduce strain on the spine.
- Weight Management – Reducing excess weight lessens pressure on the spine.
- Posture Improvement – Using ergonomic chairs and avoiding prolonged sitting.
- Quit Smoking – Improves blood flow to spinal discs.
Surgical Treatment Options
- Involves fusing two vertebrae stabilize the spine.
- Commonly performed in lumbar (lower back) and cervical (neck) spine.
- A damaged disc is replaced with an artificial implant to maintain movement.
- Recommended for younger patients who require flexibility.
- Involves smaller incisions, leading faster recovery and less postoperative pain.
- Techniques include microdiscectomy and endoscopic spine surgery.
Why Choose Nagpur for DDD Treatment?
Nagpur has become a hub for high-quality spine care due to several factors:
- Expert Spine Specialists – The city is home to experienced orthopedic surgeons and neurosurgeons.
- Advanced Medical Facilities – Hospitals in Nagpur offer state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment options.
- Affordable Healthcare – Treatment costs are lower compared to metro cities.
- Personalized Rehabilitation Programs – Tailored therapy plans for faster recovery.Contact Us
