Prostate Ultrasound
Prostate ultrasound in nagpur, also known as transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), is a non-invasive medical imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues.
During the procedure:
1. Preparation: No special preparation is required.
2. Positioning: Lie on your side with your knees bent or feet in stirrups.
3. Transducer placement: A small probe (transducer) is inserted into the rectum, close to the prostate gland.
Prostate ultrasound is employed in the following:
1. Measurement of prostate size and shape
2. Detecting prostate cancer and any other abnormalities
3. Guidance for prostate biopsy or other interventions
4. Determining prostate cancer course or response to treatment
5. Suspected prostate conditions in high-risk patients
Prostate ultrasound may help in diagnosing situations like:
1. BPH
2. Prostatitis, inflammation of the prostate
3. Prostate cancer
4. Presence of cysts or abscesses in the prostate
5. Calcification in the prostate
What Is a Prostate Ultrasound?
A prostate ultrasound, also known as a transrectal ultrasound, is a non-invasive medical imaging test that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce a detailed image of the prostate gland and other surrounding tissues. It is conducted to diagnose and monitor several conditions of the prostate, such as cancer, enlargement, and inflammation.
A small probe referred to as the transducer is inserted into the rectum, close to the prostate gland, during the prostate ultrasound. The device sends or receives sound waves and forms images on a monitor. It usually takes 15-30 minutes; the sonographer and radiologist conducts it.
Prostate ultrasound is used for:
– Assessment of size or shape of a prostate
– Determination of prostate cancer or abnormalities
– Guide biopsies or other interventional procedures
– It helps monitor the progression of prostate cancer or assess treatment response, serves as a tool for screening at-risk patients for potential prostate problems.
Prostate ultrasound is an extremely important tool for healthcare providers in the evaluation and management of prostate-related conditions.
Reasons for a Prostate Ultrasound:
- Prostate cancer screening: To evaluate the prostate for any suspicious areas or tumors.
- Prostate enlargement (BPH): To assess the size and condition of the prostate in cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Elevated PSA levels: If blood tests show high levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an ultrasound can help determine the cause.
- Guiding a biopsy: The procedure can be used to guide a needle for a prostate biopsy if cancer is suspected.
- Prostate infections: To detect inflammation or abscesses in cases of prostatitis.
Procedure:
- Preparation: Patients are typically asked to empty their bladder or may need to the undergo an enema to clear the rectum.
- Positioning: The patient lies on their side with knees bent toward the chest.
- Transducer insertion: A small, lubricated ultrasound probe (transducer) is gently inserted into the rectum, which is located close to the prostate.
- Imaging: The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the prostate gland, creating images on a monitor.
- Duration: The procedure takes around 15-30 minutes and is generally well tolerated.
Advantages:
- Guides prostate biopsy: It provides real-time imaging to ensure that biopsy samples are taken from precise areas of concern.
- Non-invasive imaging: While it involves a rectal probe, the procedure is less invasive than surgeries or other diagnostic tools.
- No radiation: The procedure uses sound waves rather than radiation, making it safe for most patients.
What is procedures of Prostate Ultrasound?
Procedures for prostate ultrasound include:
1. Preparation:
– No specific preparation exists before a patient is administered the procedure
– Wear loose-fitting clothes that allow easy exposure of a rectal area
2. Positioning:
– Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet fixed in the stirrups.
– A pillow or pad may be placed on the lower part of your hips for support
3. Transducer placement:
– A small probe is inserted through the rectum, with an insertion location close to the prostate gland
– Injection of Gel or lubricant on the transducer to assist in insertion
4. Imaging
– The sonographer may adjust the transducer, and images are captured from different angles
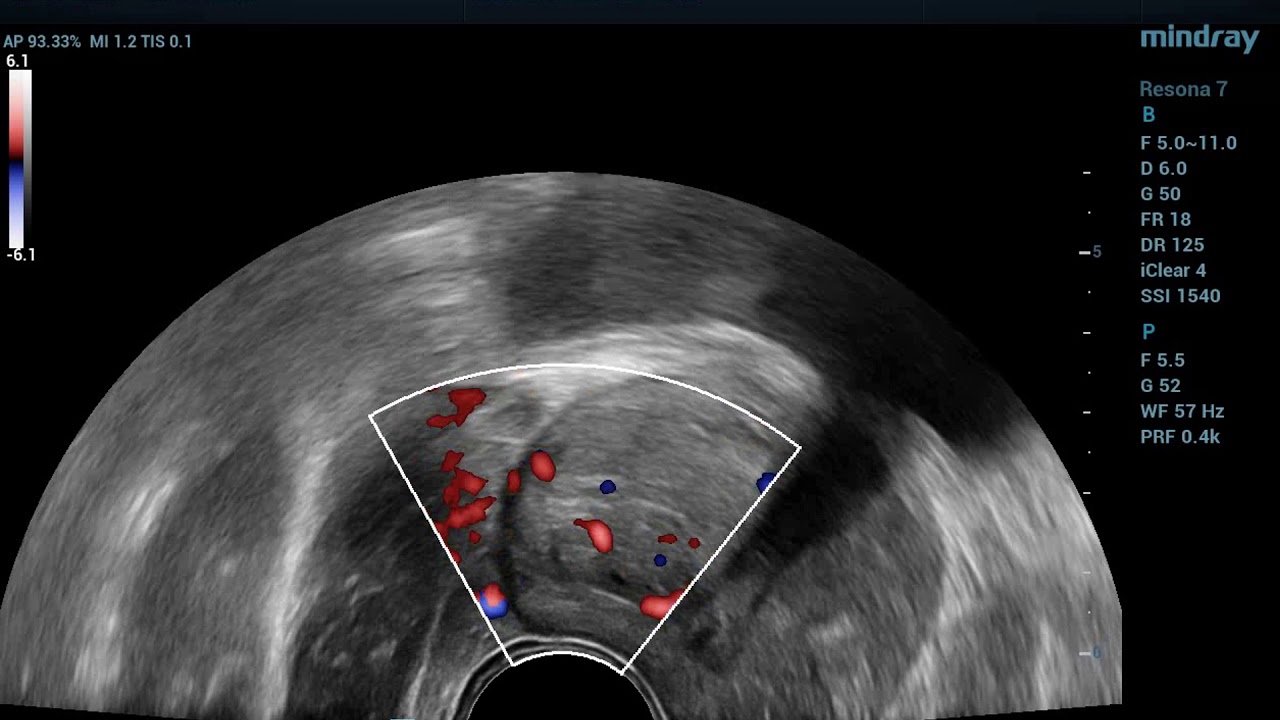
5. Doppler assessment
– Evaluation of flow in blood in the gland or a tissues surrounding the prostate
6. Image interpretation
The sonographer or radiologist studies the images and measurements
7. Reporting
– A written report with findings and suggestions for either the gland or tissues surrounding the gland
8. Other procedures if need be
– FNAB: prostate biopsy
– Surgery of the prostate
9. After Treatment:
– Return to normal activities immediately
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
