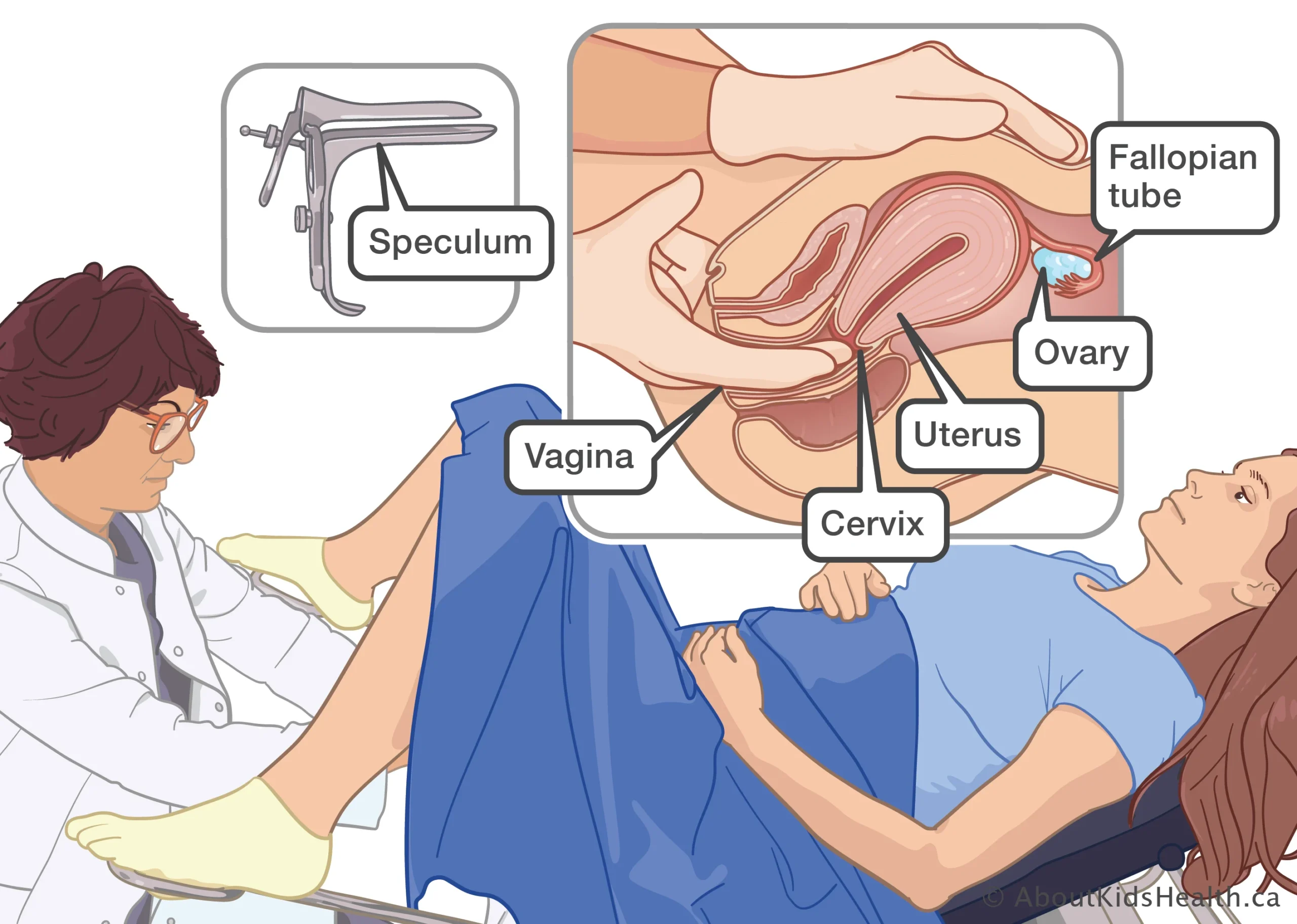
Pelvic exams
The pelvic exams are important for women’s health care because they check the female reproductive system and confirm whether there is a health issue that has not been noticed. Here’s what you need to know:
What happens during a pelvic exam?
1. External and internal visual examination :The provider will visually examine the vulva and vagina.
2. Speculum insertion: A speculum is slowly inserted into the vagina for a clear view of the cervix and vagina.
3. Cervical screening: A Pap smear or HPV test may be conducted to determine the presence of cervical cancer or precancerous cells.
Why do pelvic exams need to be performed?
1. Cervical cancer screening
2. Evaluation of anatomical abnormality in a reproductive system
3. Assessment of menstrual disorder
4. Identification and investigation of pain or discomfort in the pelvic region
5. STI screening
How often does a pelvic exam need to be done?
1. Annual check-up: All women aged between 21 and 65 years.
2. Every three years: All women aged between 30 and 65 years who have had normal Pap smears for the past three consecutive years.
Remember, such an examination is regarded as a part of women’s overall health care. To be informed and comfortable is definitely key to a good experience for any pelvic exam. Don’t be afraid to ask your healthcare provider questions or concerns!
What Is a Pelvic exams?
A pelvic exam is a medical checkup of the female reproductive organ, which is constituted by inspecting and checking the vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, ovaries, and rectum. It is normally performed by a medical doctor, such as a gynecologist or primary care physician, to ensure proper reproductive health and identify any anomaly.
The health-care provider will:
1. Visually examine the vulva and vagina
2. Introduce a speculum into the vagina so that you can see the cervix or vagina
3. Perform a bimanual exam where you insert two gloved fingers into the vagina and press on the abdomen so that you can feel the uterus, ovaries, and cervix
4. Perform a rectovaginal exam by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum to check for abnormalities.
Pelvic exams are used for:
1. Screening of cervical cancer and precancerous cells.
2. Those disorders of the reproductive system, as in fibroids or cysts.
3. Disorders in menstruations like unregulated cycle and heavy bleeding during menstruation.
4. Examine for painful or aching sensations in the pelvis.
5. Screening for sexually transmitted infections
A pelvic exam is a fundamental part of gynecologic care and should be part of yearly check-ups with a healthcare provider for women between the ages of 21 and 65 years.
Purpose of a Pelvic Exam
A pelvic exam serves several important purposes, including:
- Routine Health Check: It allows healthcare providers to monitor reproductive health and identify any abnormalities early.
- Screening for Diseases: Helps detect conditions such as:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Cervical cancer (often in conjunction with the Pap smear)
- Uterine abnormalities (fibroids, polyps)
- Ovarian cysts
- Assessing Symptoms: Evaluating specific symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or unusual discharge.
- Contraceptive Counseling: Providing guidance on birth control options and reproductive health.
What to Expect During a Pelvic Exam
- Preparation:
- Schedule the exam when you are a not menstruating, if a possible.
- Avoid vaginal intercourse, douching, or using tampons for 24-48 hours prior to the exam to ensure accurate results.
- The Exam Process:
- Medical History: Your provider will ask about your medical history, menstrual cycle, sexual activity, and any symptoms or concerns you may have.
- Physical Exam: You will be asked to undress from the waist down and lie on an examination table, typically with your feet in stirrups.
- External Exam: The provider will inspect the external genitalia for any abnormalities or signs of infection.
- Internal Exam:
- A speculum (a small device that opens the vagina) will be gently inserted to visualize the cervix and vaginal walls.
- The provider may collect samples for a Pap smear or STI testing during this stage.
- A bimanual exam may follow, where the provider inserts two fingers into the vagina while pressing on the abdomen to assess the uterus and ovaries for size, shape, and tenderness.
- Duration: The entire pelvic exam typically lasts about the 10 to 20 minutes.
Aftercare
- Post-Exam Symptoms: It is normal to experience mild cramping or spotting after the exam, especially if a Pap smear was performed. However, significant pain or heavy bleeding should be reported to your healthcare provider.
- Results: You will usually receive the results of any tests conducted during the exam within a few days to weeks. Follow up with your provider if you have any questions or concerns about your results.
Frequency of Pelvic Exams
- Routine Check-Ups: Most women should have their first pelvic exam between the ages of 21 and 29, regardless of sexual activity. The frequency of subsequent exams may vary based on age, health history, and risk factors, but typically every 1-3 years is recommended.
- Individualized Care: Women with specific health concerns or risk factors may need more frequent exams or additional screenings.
What is procedures Pelvic exams?
Pelvic Exam Procedures include the following:
1. Visual Inspection:
-Looks for any abnormalities of the vulva, vagina, and cervix.
2. Speculum Examination:
-Uses a speculum to view the cervix and vagina by introducing it into the vagina.
3. Bimanual Examination:
-Inserts two gloved fingers into the vagina and presses onto the abdomen to palpate the uterus, ovaries, and cervix.
4. Rectovaginal Examination:
-Introduces a gloved finger into the rectum in order to detect whether or not there is some anomaly.
5. Pap Smear:
-Collection of a sample of cells from the cervix to check for cervical cancer.
6. HPV Test:
-Taking a sample of cells from the cervix for the detection of high-risk types of HPV.
7. Pelvic Ultrasound:
-It refers to viewing of the reproductive organs with ultrasound waves.
8. Endometrial Biopsy:
-This is collection of a sample of tissue of the lining of the uterus.
9. Colposcopy:
-This is the use of a special microscope to check the cervix or vagina for abnormalities.
10. Cryotherapy:
– Freezing abnormal cells to kill.
These investigations are conducted for:
– Cervical cancer or the existence of precancerous cells
– Inspection of abnormalities in the reproductive systems
– Evaluation of menstrual disorders
– Investigation of pelvic pain or aching
– Detection of STIs
Note: The procedures may differ with each patient and depends on the health care provider’s discretion.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
