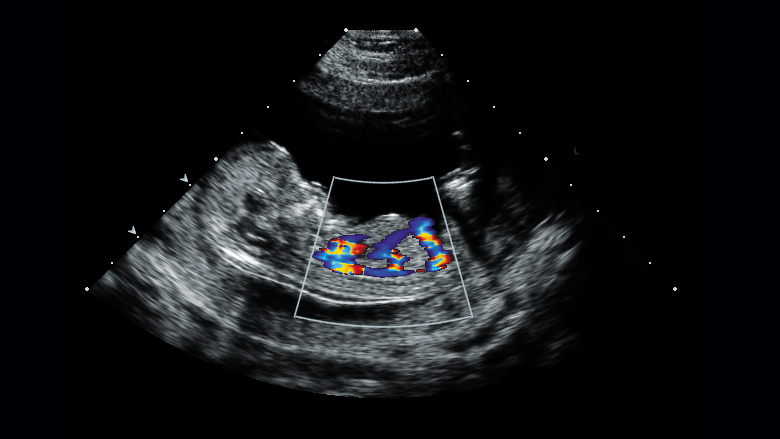
Fetal echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography: It is a high resolution ultrasound scan that diagnoses the anatomy and physiology of the fetal heart. Aspects covered include: Theoretical background
1. Physics:- Ultrasound waves and frequencies
2. Anatomy:- Development and anatomy of the fetal heart
3. Physiology:- Fetal cardiac function and hemodynamics
4. Pathology:- Congenital heart defects (CHDs) and its classification
5. Diagnostic criteria:- Normal and abnormal fetal heart findings
6. Clinical applications:- Assessment and monitoring of the fetal heart
7. Studies and advancements:- Development and working of fetal heart
In this context, it becomes crucial for a health care provider to be aware of those theoretical concepts so that they can interpret proper images of fetal echocardiography and appropriately manage fetuses with cardiac anomalies.
Fetal echocardiography refers to a highly specific ultrasound exam that especially involves the fetus’ heart. This procedure is a used in the following fields:
1. Assessment of the anatomical and functional entities of the fetal heart.
2. Diagnosis of congenital defects of the heart.
3. Monitoring of the fetal heart rhythm and rate.
4. Assessment of the fetal cardiac function and well-being.
5. Instructive fetal therapy and intervention.
Procedure of the procedure:
1. Specialized ultrasound machines utilized
2. Probe or transducer placed on the mother’s belly
3. High frequency sound waves emitted through the uterus
4. Fetal heart seen in real time
5. Images and videos recorded for analysis
Fetal echocardiography can diagnose most heart abnormalities, such as;
1. Septal defects
2. Valve deformity
3. Distension of cardiac chambers
4. Cardiac arrhythmia
5. Cardiac tumor
The fetal echocardiography is performed between 16 and 24 weeks; however, the process can be done before or after completion of the 24 weeks pregnancy.
Fetal echocardiography has proven to be extremely useful in the diagnosis process of the following conditions:
Early detection of CHDs.
Guiding fetal therapy and intervention.
Planning postnatal care and management.
Improving the outcome of fetuses with CHDs.
Note: Fetal echocardiography is a specialist examination requiring knowledge of fetal cardiology or ultrasound.
What Is a Fetal echocardiography?
Fetal echocardiography, also known as high-resolution fetal echocardiography, is an ultrasound scan which utilises high-frequency sound waves to produce highly detailed images of the fetus’s heart. It is a noninvasive investigation which studies in detail the structure and function of the fetal heart, thus facilitating the diagnosis and monitoring of congenital heart defects (CHDs) and other anomalies of the heart.
Fetal echocardiography typically encompasses:
2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound imaging
Colour Doppler and spectral Doppler analysis
3. Cardiac structure, Function, and blood flow evaluation.
4. Evaluation of cardiac rhythm and rate
This is typically performed between 16-24 weeks of gestation but can be done much earlier or even later than this range is needed. Fetal echocardiography is the absolutely indispensable in the following instances :
1. Early Diagnosis of CHDs.
2. Fetal therapy and intervention.
3. Planning of postnatal care and management.
4. Better outcomes for fetuses with heart anomalies.
Fetal echocardiography is, therefore, an essential component of care for fetuses with cardiac disorders, thus assisting healthcare providers in making informed decisions and giving the best possible care.Fetal echocardiography, also known as high-resolution fetal echocardiography, is an ultrasound scan which employs high-frequency sound waves in order to produce highly detailed images of the fetus’s heart. This is a non-invasive evaluation that analyzes the anatomy and physiology of the fetal heart in detail and thereby makes possible diagnosis and monitoring in congenital heart defects (CHDs) or other anomalies of the heart.
Fetal echocardiography commonly includes:
2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound imaging
Colour Doppler and spectral Doppler analysis
3. Evaluation of cardiac structure, function and haemodynamics.
4. Evaluation of cardiac rhythm and rate
This is normally performed between 16-24 weeks of gestation but can be offered much earlier or later than this range is needed. Fetal echocardiography is absolutely essential in the following scenarios :
1. Early Diagnosis of CHDs .
2. Fetal therapy and intervention .
3. Planning for postnatal care and management.
4. Better outcomes for pregnancies affected by anomalies in the heart
Fetal echocardiography is, consequently, an integral aspect of care for fetuses with cardiac disorders, hence supporting providers in making enlightened decisions and providing the best possible care.
Indications for Fetal Echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography is recommended in several situations, including:
- Family History:
- A family history of congenital heart defects or genetic syndromes that may affect the heart.
- Maternal Health Conditions:
- Maternal conditions such as diabetes, lupus, or certain medications that may increase the risk of heart defects.
- Abnormal Findings on Standard Ultrasound:
- Anomaly detected in routine ultrasound scans, such as structural abnormalities or signs of growth restriction.
- Arrhythmias:
- If there are signs of fetal arrhythmias or abnormal fetal heart rate patterns during monitoring.
- Previous Pregnancy Complications:
- If there was a history of congenital heart defects or other cardiac anomalies in previous pregnancies.
- Multiple Pregnancies:
- To assess the heart function and structure in twins or higher-order multiples, especially in cases of twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS).
Procedure of Fetal Echocardiography
- Preparation:
- The mother may be asked to drink water before the procedure to ensure a full bladder, which can help improve imaging quality.
- Positioning:
- The mother lies on her back or side, and a gel is applied to her abdomen to facilitate the transmission of sound waves.
- Imaging:
- A transducer is placed on the abdomen, and sound waves are emitted, creating real-time images of the fetus’s heart.
- The sonographer or physician will evaluate the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels, assessing size, shape, and function.
- Special views, such as the four-chamber view and outflow tract views, are obtained to check for abnormalities.
- Color Doppler Imaging:
- This technique may be used to visualize blood flow through the heart and major vessels, allowing for assessment of valve function and potential obstructions.
What to Expect
- The procedure typically lasts 30 to 60 minutes, depending on a complexity of the evaluation.
- The mother may receive immediate feedback about the findings, but a detailed report will usually be provided later.
- If any abnormalities are detected, the healthcare provider will discuss the implications and potential next steps, which may include further testing or referrals to pediatric cardiologists.
Benefits of Fetal Echocardiography
- Early Detection: Allows for early diagnosis of congenital heart defects, which can lead to timely intervention and management strategies.
- Informed Decision-Making: Provides crucial information for parents and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about delivery and postnatal care.
- Monitoring: Enables ongoing monitoring of known cardiac conditions throughout pregnancy.
Purpose of Fetal Echocardiography:
- Detect congenital heart defects (CHDs): It can identify structural problems like holes in the heart, abnormal valves, or issues with the heart chambers.
- Assess heart function: It evaluates how well the heart is pumping and how the blood flows through the heart and major vessels.
- Diagnose rhythm problems: It can detect abnormal heartbeats or arrhythmias in the fetus.
- Guide treatment: In some cases, knowing about heart problems early allows for planning specialized care after birth, or even in utero intervention if necessary.
Who Needs a Fetal Echocardiogram?
It’s not a routine test for all pregnancies but may be a recommended if:
- Family history of congenital heart defects.
- Abnormal ultrasound findings suggest heart issues.
- Increased risk factors such as:
- Mother with diabetes or lupus.
- Genetic conditions (like Down syndrome).
- Exposure to certain infections (like rubella) or medications during pregnancy.
- Abnormal fetal heart rate and irregular heartbeat detected during a routine ultrasound.
- Twin or multiple pregnancies with increased risk of complications.
What procedures Fetal echocardiography?
Fetal Echocardiography involves the following:
1. Preparation
– The abdomen is cleaned and gel applied.
– The probe is called transducer, which is placed on the abdomen.
2. Imaging
– 2D, 3D, and 4D ultrasound images.
– The structures and flow of blood in the cardiac are imaged.
3. Doppler analysis
– Color Doppler is applied in the studies of flow or velocity.
– Spectral Doppler monitors the velocities of blood as well as gradients.
4. Cardiac assessment
– The studies of the functions and structures of the cardiac
– Exploration of heart chambers, valves, and vessels
5. Rhythm evaluation:
– Evaluation of the fetus heart rhythm and rate
6. Image capture:
– Images and video are captured for evaluation
7. Interpretation:
– Images are interpreted by a fetal cardiologist or radiologist with diagnosis and report
8. Follow-up:
– More can be pursued to explore the development and function of fetal cardiac Procedures associated with fetal echocardiography vary from case to case and even with the preference of the health provider.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
