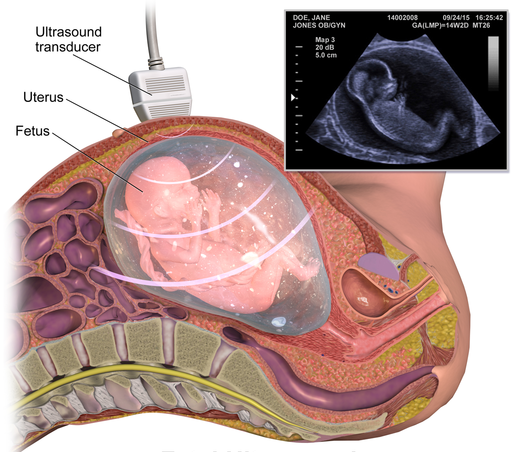
Fetal imaging
Fetal imaging in Nagpur applies medical imaging technologies to the fetus. Generally, the purpose of fetal imaging is to:
1. Monitor the growth and development of a fetus.
2. Diagnose any anomalies or congenital abnormalities in a fetus.
3. Serve as a guide in the procedures during fetal therapy and intervention.
4. Assess the status of a fetus with an objective of observing complications.
General uses of fetal imaging are:
1. Ultrasound (US): It is an imaging test that uses sound waves to look at pictures of body organs, tissues, and other structures.
2. Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This scan creates detailed images of the fetus by using magnetic fields and radio waves.
3. Fetal Computed Tomography (CT): It is utilized in producing cross-sectional images of the fetus by applying X-rays with computer technologies.
It is generally applied in scenarios like:
1. Diagnosis of congenital anomalies, such as heart defects or neural tube defects.
2. Monitoring and diagnosing growth restrictions.
3. Guiding fetal therapy, which might involve blood transfusions or the placement of a shunt.
4. Diagnosing and assessing fetal well-being and any signs of distress.
5. Planning postnatal care and potential surgeries.
Fetal imaging is usually carried out by a healthcare provider or a dedicated fetal imaging center, and the modality selected in a particular clinical indication and gestational age would determine it.
What Is a Fetal imaging?
Fetal imaging involves the use of medical imaging technologies in imaging and detect the fetus during pregnancy. It will enable care providers to:
1. Assess the size and development of the fetus.
2. Diagnose congenital anomalies or abnormalities
3. Perform procedures that can support fetal therapy and intervention.
4. Continuously update the well-being status of the fetus, avoiding further complications.
There are various types of fetal imaging modalities, including:
1. Ultrasound
2. Fetal MRI
3. CT
4. Doppler Ultrasound
5. 3D and 4D Ultrasound
Fetal imaging is required in the following:
1. Prenatal diagnosis and treatment
2. Monitoring growth or developments of the fetus
3. Potential complications detection
4. Fetal therapy or intervention planning
5. Planning for postnatal care and possible surgeries
Fetal imaging enables healthcare professionals to do the following:
1. Diagnose congenital anomalies
2. Monitor fetal growth restrictions
3. Detect fetal distress
4. Guide fetal surgery or intervention
5. Plan for postnatal care and management
Overall, fetal imaging is therefore important in achieving healthy and well-preserved fetuses in cases of pregnancy.
Common Fetal Imaging Techniques
- Ultrasound:
- Standard Ultrasound: The most common imaging method during pregnancy, using high-frequency sound waves to create images of the fetus and surrounding structures. It can be performed in different trimesters for various purposes:
- First Trimester: To confirm pregnancy, assess gestational age, and check for multiple pregnancies.
- Second Trimester: Often includes a detailed anatomy scan around 18-20 weeks to evaluate fetal growth and detect structural anomalies.
- Third Trimester: To monitor fetal growth, position, and well-being as the delivery date approaches.
- Doppler Ultrasound: A specialized ultrasound that assesses blood flow in the fetus and placenta. It is particularly useful in monitoring conditions like intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS).
- Standard Ultrasound: The most common imaging method during pregnancy, using high-frequency sound waves to create images of the fetus and surrounding structures. It can be performed in different trimesters for various purposes:
- Fetal Echocardiography:
- A specialized ultrasound focused on assessing the fetal heart’s structure and function. It is typically performed between 18 and 24 weeks of pregnancy to detect congenital heart defects or other cardiac abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
- Fetal MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the fetus and surrounding tissues. It is especially useful for assessing complex anomalies, brain development, and conditions not well visualized on ultrasound. MRI is typically performed in the second or third trimester and is used when more information is needed beyond what ultrasound can provide.
- 3D and 4D Ultrasound:
- 3D Ultrasound: Provides three-dimensional images of the fetus, allowing for better visualization of anatomical structures and abnormalities.
- 4D Ultrasound: A dynamic form of 3D imaging that shows live images of the fetus in motion, providing a more interactive view of fetal movements and expressions.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT):
- Although not a traditional imaging technique, NIPT analyzes cell-free fetal DNA from the mother’s blood to screen for certain genetic conditions (e.g., Down syndrome). While it does not provide imaging, it complements imaging techniques by assessing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Indications for Fetal Imaging
Fetal imaging may be recommended for various reasons, including:
- Routine Screening: To monitor normal fetal growth and development throughout the pregnancy.
- Anomaly Detection: To identify potential structural or functional abnormalities in the fetus.
- Monitoring High-Risk Pregnancies: For mothers with pre-existing conditions, complications, or a history of previous pregnancies with issues.
- Assessment of Multiple Pregnancies: To monitor twins, triplets, or higher-order multiples for complications like TTTS.
- Evaluating Specific Concerns: If there are concerns about fetal movements, size, or maternal health conditions affecting the fetus.
Benefits of Fetal Imaging
- Early Detection: Imaging allows for the early identification of potential abnormalities, enabling timely interventions and management.
- Monitoring Fetal Health: Regular imaging helps track fetal growth and development, ensuring the fetus is healthy and thriving.
- Informed Decision-Making: Fetal imaging provides essential information for healthcare providers and families, helping them make informed choices about care and potential interventions.
- Preparation for Delivery: Detailed imaging can help plan for any necessary care or interventions needed immediately after birth.
Risks and Considerations
- Ultrasound: Generally considered safe and non-invasive, but healthcare providers follow guidelines to minimize exposure and perform only necessary scans.
- MRI: Also considered safe during pregnancy, but it should be performed with caution and only when the benefits outweigh potential risks.
- Doppler Studies: Should be performed with caution, especially in high-risk pregnancies, to avoid unnecessary exposure.
What procedures Fetal imaging?
This includes:
1. Ultrasound (US):
-2D, 3D and 4D ultrasound
-Doppler ultrasound
-Fetal echocardiography
2. Fetal Magnetic Resonance -Imaging (MRI):
-Structural MRI
-Functional MRI, such as the fetal heart rate monitoring
3. Fetal Computed Tomography (CT):
-Low dose CT scans
4. Fetal X-ray:
-Special techniques are used by the radiologist if an x-ray cannot be delayed until after pregnancy. The radiation exposure on the fetus is minimized.
5. Fetal Echocardiography:
-It covers detailed ultrasound before birth for evaluation of a congenital heart defect.
6. Fetal Cardiac MRI:
-It is a detailed imaging of the structures and function of the fetal heart.
7. Fetal Brain MRI:
-It is detailed imaging of the structures and development of the fetal brain.
8. Fetal Body MRI:
-Imaging of other organs and body parts of the fetus
9. Placental MRI:
-It covers imaging of the placenta and its function
10. Fetal Growth Ultrasound:
-The scans should be viewed from the medical point and the duration should be up to half an hour.
The procedures are used in order to;
- Diagnose the congenital anomalies
- Monitor the growth or development of the fetus
- Assessment of the condition or complications of the fetus
- To guide fetal therapy or interventions
- To plan postnatal care and management
End.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
