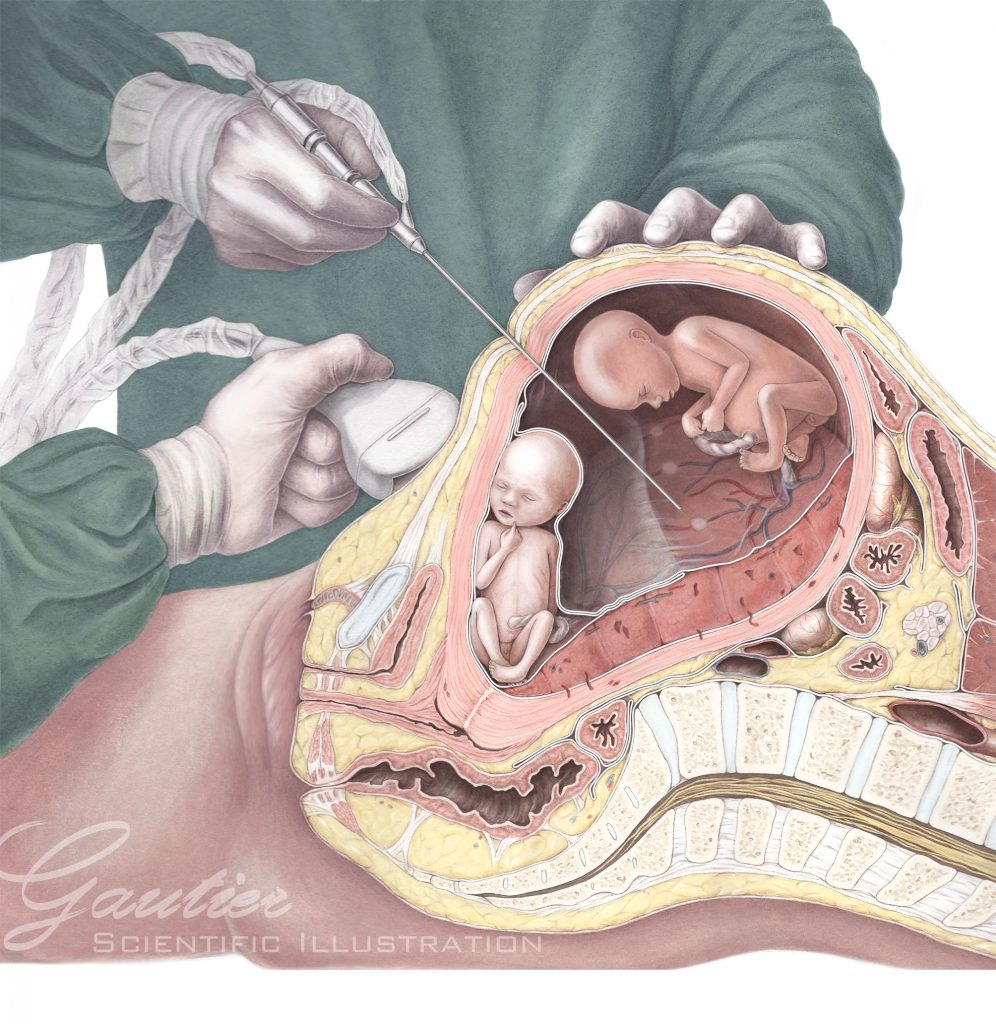
Fetal therapy
Fetal therapy in Nagpur: This actually involves treatments and interventions performed on the fetus while still in the womb. The primary purpose of fetal therapy is to enhance the health and well-being of the fetus. In some cases, the goal is to save the life of the fetus.
Fetal therapy includes several conditions such as:
1. Fetal anemia
2. Fetal heart defects
3. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
4. Fetal growth restriction
5. Congenital anomalies
Types of fetal therapy:
1. Transfusions intrauterine: The transfusion directly administered to the fetus.
2. Fetal shunt placement: Removal of excessive amount of fluid from the fetus.
3. Fetal surgery: Any type of surgery to be conducted within the womb.
4. Radiofrequency ablation: Conducted for twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
5. Laser therapy: To treat twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome.
6. Fetal medication: Administered to the mother so that she passes on to the fetus.
7. Fetal cardiac therapy: Done in case there are any problems with the heart of the fetus.
8. Fetal neurotherapy : Treatments for fetal neurofunctional conditions.
What Is a Fetal therapy?
Fetal therapy is also known as prenatal or intrauterine therapy. These are medical treatments and interventions carried out on the fetus while the baby is still in the womb with a view to:
1. Diagnosing and treating fetal anomalies or conditions.
2. Regulating growth and development of the fetus.
3. Eliminating complications that the pregnancy may have faced.
4. Enhanced well-being of the fetus or delivery outcomes.
Methods for fetal therapy might include medication given to the mother so that the drugs can be a cross the placental barrier or reach the fetus.
2. Procedures performed inside the uterus, including blood transfusion or shunt placement
3. Operations conducted on the fetus, such as fetal surgery or laser treatment.
Fetal therapy is undertaken to enhance fetal health and well-being and to reduce complications while improving the mother’s and the baby’s chances.
A few of the more common conditions treated with fetal therapy are:
1. Fetal anemia
2. Fetal heart defects
3. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
4. Fetal growth restriction
5. Congenital anomalies
6. Fetal infections
7. Fetal arrhythmias
Fetal treatment is offered by a multidisciplinary healthcare team such as maternal-fetal medicine specialists, pediatric surgeons and other specialists.
Types of Fetal Therapy
- In-Utero Surgery:
- Open Surgery: This involves accessing the uterus through an incision in the mother’s abdomen. It is typically used for the conditions like:
- Spina Bifida: A neural tube defect where the spinal column does not close completely, leading to potential neurological issues. Fetal surgery can repair the defect before birth.
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: A condition where abdominal organs move into the chest cavity, affecting lung development. Surgery may help to reposition these organs.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques like fetoscopy (using a thin tube with a camera) allow for procedures without a large incision. These may include:
- Laser Surgery: Used for conditions like twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), where blood flow is unbalanced between twins. Laser therapy can help separate shared blood vessels in the placenta.
- Open Surgery: This involves accessing the uterus through an incision in the mother’s abdomen. It is typically used for the conditions like:
- Fetal Blood Transfusion:
- This procedure is used for conditions like Rh disease or fetal anemia. It involves transfusing blood into the fetus through the umbilical cord to treat low hemoglobin levels.
- Amnioreduction:
- In cases of polyhydramnios (excess amniotic fluid), amnioreduction can relieve pressure on the mother and fetus by removing excess fluid from the amniotic sac.
- Fetal Ablation:
- This procedure is used to treat certain types of fetal arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). A laser may be used to destroy abnormal heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
- Medication Administration:
- In some cases, medications can be administered to the fetus through the mother or directly into the amniotic sac. For example, steroids can be given to help mature fetal lungs in cases of preterm labor.
- Gene Therapy (Emerging Field):
- Experimental approaches to deliver genes that may correct genetic disorders are being researched, but this is still in the early stages and not widely available.
Indications for Fetal Therapy
Fetal therapy may be considered for a variety of conditions, including but not limited to:
- Neural Tube Defects: Such as spina bifida.
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Affecting lung development.
- Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome: In identical twins sharing a placenta.
- Fetal Anemia: Due to Rh disease or other causes.
- Severe Congenital Heart Defects: Where immediate intervention may improve outcomes.
- Cleft Lip and Palate: In certain cases, interventions can improve outcomes.
- Fetal Tumors: Such as teratomas that may require removal.
Risks and Considerations
Fetal therapy is not without risks. Potential complications can include:
- Preterm Labor: Increased risk of premature delivery following certain procedures.
- Infection: Introduction of infection into the uterus can pose risks to both mother and fetus.
- Placental Abruption: Premature separation of a placenta from a uterine wall.
- Fetal Injury: Potential harm to the fetus during surgical procedures.
- Maternal Complications: Anesthesia and surgery can pose risks to the mother.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Fetal therapy often involves a team of specialists, including:
- Maternal-Fetal Medicine Specialists: To manage high-risk pregnancies and perform procedures.
- Pediatric Surgeons: For surgical interventions after birth.
- Neonatologists: For care of the newborn following delivery.
- Genetic Counselors: To assist with understanding genetic implications and risks.
- Anesthesiologists: To manage anesthesia for surgical procedures.
What procedures Fetal therapy?
The other fetal therapy procedures include:
1. Intrauterine transfusions (IUT): this is the direct infusion of blood into the fetus
2. Fetal shunt placement: it involved the drainage of excess fluid from the fetus
3. Fetal surgery: surgies performed on the fetus, this includes correction of congenital anomalies
4. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA): a treatment for a twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
5. Laser therapy: a treatment for a twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome
6. Fetal medication: drugs given to the mother for the treatment of the fetus.
7. Fetal cardiac therapy : Therapy for fetal heart conditions, such as arrhythmias.
8. Fetal neurotherapy : Therapy for fetal neurological conditions, such as hydrocephalus.
9. Amnioreduction : Removing excess amniotic fluid.
10. Fetal blood sampling : Sampling of fetal blood for examination or diagnosis.
11. Intrauterine exchange transfusion : Replacement of the fetus’s blood with donor blood.
12. Fetal endoscopic surgery : Minimal invasive surgery using endoscopes.
13. Open fetal surgery : Surgical procedures with a wider incision.
14. MRI-guided procedures of fetus: Procedures like fetoscopic surgery guided using MRI.
15. Fetal cardiac intervention: Procedures like balloon valvuloplasty for heart defects.
These procedures can be done to treat various congenital anomalies, fetal growth restriction, twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome, fetal infections, fetal arrhythmias, hydrocephalus, among other conditions.
Do note that all the procedures and frequencies mentioned above are to vary with each case and recommendations from health care providers.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
