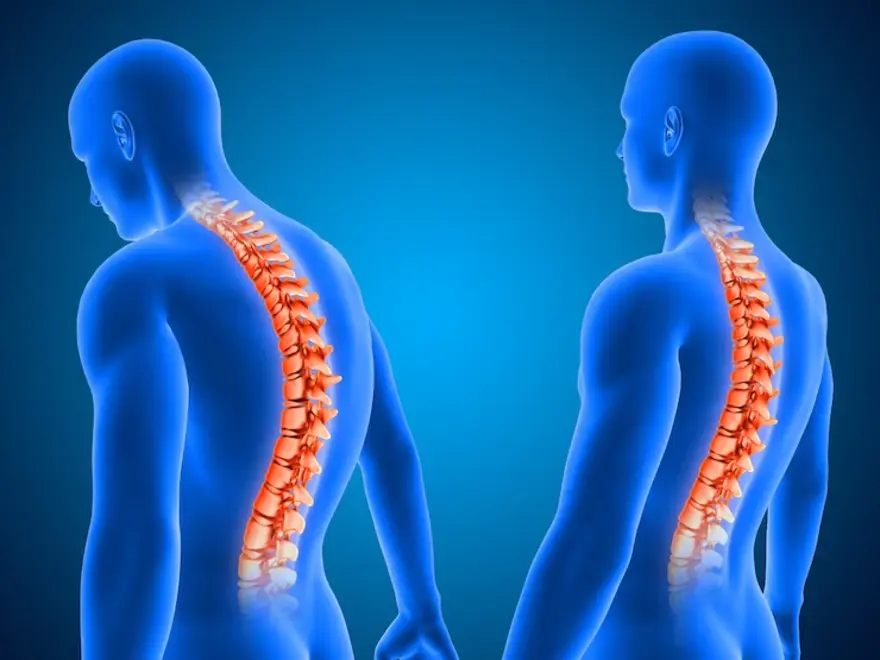
Kyphosis
Kyphosis in Nagpur is a spina curvatura when the upper back of someone curves abnormally due to which the front curve of their upper back, also referred to as the thoracic spine, rounds forwards. People of all ages, from children through adults will be affected.
Types of Kyphosis:
1. Postural Kyphosis : This is due to poor posture habits.
2. Scheuermann’s Kyphosis: A condition that some people are born with and affects teenagers.
3. Degenerative Kyphosis: This is due to wear and tear of the spine. It occurs mainly in older adults.
4. Compression Fracture Kyphosis: due to spinal fractures.
5. Congenital Kyphosis: present at birth.
Kyphosis is an exaggerated transfer curvature of the upper back. In aged individuals, kyphosis typically results from weakness in the bones of the spine that leads them to collapse or fracture. There are several forms of kyphosis that may occur during infancy or adolescence. Such forms stem from congenital malformation of the spine or gradual wedging of the bones of the spine over time.
Features:
- Forward slouching or curvature of the upper back
- Back pain,
- Lack of flexibility
- In extreme cases: Dyspnea
What Is a Kyphosis ?
It is the abnormal curvature of the spine, which is very often acquired in the form of an abnormal forward curvature, creating a hunched or rounded back. Any area of the spine can be involved but most commonly affects the thoracic and lumbar areas of the spine.
4. Compression fracture kyphosis (fractures in the spine)
5. Congenital kyphosis (from birth)
Kyphosis leads to:
Back ache
Rigidity
Can’t keep straight standing or sitting upright
In extreme, breathing is difficult
Psychological distress; cosmetic related
If left untreated, kyphosis gives complications like:
Respiratory
Cardiovascular
Increased risk of fractures in the spine
Decreased mobility and flexibility
Treatment is usually bracing or physical therapy alone but may include surgery in more extreme cases of kyphosis.
Types of Kyphosis:
- Postural Kyphosis:
- Most common type, often seen in adolescents and young adults.
- Caused by poor posture, leading to the muscles and ligaments of the spine becoming overstretched.
- Generally mild and flexible, meaning the curve can improve with better posture and exercise.
- No structural abnormalities in the vertebrae.
- Typically doesn’t cause significant pain or long-term complications.
- Scheuermann’s Kyphosis (Scheuermann’s Disease):
- More severe than postural kyphosis, often diagnosed during adolescence.
- Caused by a structural abnormality where the vertebrae grow unevenly, resulting in wedge-shaped vertebrae.
- The curve is rigid, meaning it cannot be corrected by posture alone.
- Patients may experience pain in the upper or mid-back, and the deformity is more pronounced than in postural kyphosis.
- In some cases, it can lead to breathing difficulties or neurological symptoms if the curve is severe.
- Congenital Kyphosis:
- Present at birth and caused by malformations of the vertebrae during fetal development.
- The spinal deformity tends to worsen as the child grows, and surgery is often required to correct the curvature.
- If untreated, it can lead to severe spinal deformities, neurological issues, or even affect organ function (such as the heart and lungs).
- Age-Related (Degenerative) Kyphosis:
- Occurs in older adults due to age-related wear and tear, particularly from osteoporosis, which weakens the vertebrae.
- Vertebral fractures, often caused by osteoporosis, lead to the spine collapsing and curving forward.
- Degenerative kyphosis may also develop in people with degenerative disc disease or arthritis.
- Can cause chronic pain, reduced mobility, and a significant impact on quality of life.
- Neuromuscular Kyphosis:
- Occurs as a result of neuromuscular disorders such as muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, or spina bifida.
- These conditions affect the muscles that support the spine, leading to abnormal curvatures.
Symptoms of Kyphosis:
- Visible curvature of the back: The main complaint is an excessive anterior curve of the spine.
- Backache: There could be moderate to severe pain in the upper back in more significant cases.
- Stiffness and spasticity: Flexibility of the spine might be decreased, and stiff, thereby rendering movement troublesome.
- Fatigue: Muscle tiredness, as the abnormal curvature of the spine may be straining the muscles around the back.
- Balance and mobility disorders: Serious cases may lead to an inability to walk or even severely affect the balance of the patient.
- Difficulty breathing: At worst, an extreme curvature can squeeze the lungs, causing difficulties with breathing.
- Numbness or weakness: Once spinal nerves or the spinal cord become compressed by the kyphosis, neurological symptoms start appearing, such as numbness, weakness, or tingling in the limbs.
Treatment of Kyphosis:
- Treatment depends on the type of kyphosis, the severity of the curvature, the patient’s age, and symptoms.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments:
For mild to moderate cases, especially in postural kyphosis or early stages of Scheuermann’s kyphosis:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises focused on strengthening the back and core muscles can improve posture and relieve pain. Stretching exercises help maintain flexibility.
- Bracing: For growing children or adolescents with Scheuermann’s kyphosis, wearing a brace may prevent the curve from worsening. The brace is typically worn until the child reaches skeletal maturity.
- Pain Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Osteoporosis Treatment: For age-related kyphosis, treating underlying osteoporosis with calcium supplements, vitamin D, and medications like bisphosphonates can help prevent further vertebral fractures.
2. Surgical Treatments:
Surgery is generally considered for severe kyphosis, especially if it causes significant pain, neurological symptoms, or affects the heart and lungs.
- Spinal Fusion: The most common surgery for kyphosis, it involves fusing two or more vertebrae together to straighten and stabilize the spine. Metal rods, screws, or bone grafts are often used to hold the vertebrae in the correct position as they heal and fuse together.
- Osteotomy: In some cases, part of the vertebrae may be removed or reshaped (an osteotomy) to reduce the kyphotic curve before spinal fusion.
- Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty: For fractures caused by osteoporosis, these minimally invasive procedures involve injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebrae to stabilize them and reduce pain.
What procedures Kyphosis?
As from the various procedures in the treatment of Kyphosis, the following procedures are listed below;
1. Observations and monitoring
2. Physiotherapy comprising of exercise and stretching
3. Bracing which is wearing a brace to stabilize the spine
4. Pain management through medication and injections
5. Spinal fusion surgery where joining two or more vertebrae comprises of
6. Instrumentation surgery that uses rods screws or any instrument to stabilize the spine
7. Osteotomy surgery where the vertebrae cuts and realign
8. Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty surgery that strengthens compressed vertebra
9. Spinal osteotomies cutting and realign the spine
10. Resection of a segment of the vertebral column
Surgery of the kyphosis aims at:
1. Correction of the curvature
2. Spinal stabilization
3. Relief of pressure upon the spinal cord and nerves
4. Anatomically pleasing posture restored, erect attitude
5. Painlessness and comfort
This would depend on the nature and degree of the Kyphosis, but it also depends on the general health condition of the patient. Thus, it ought to be evaluated by a professional healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist that could then create an effective treatment plan for this condition.
At our Neurosys Multispeciality Center, we perform several key procedures including Craniotomy, which is primarily for the excision of brain tumors; V-P Shunt Surgery for treating hydrocephalus; surgeries for epilepsy; and operations targeting brain stem glioma. Beyond these, we offer a range of other neurosurgical services. If you have any questions that are not answere, please contact us through our Contact Us or Book your Appointment.
